Power outages can transform your home from a comfortable sanctuary into an uninhabitable space within minutes. When the lights go out during a severe storm, the urgency to restore electricity becomes overwhelming—especially when you consider spoiled food, frozen pipes, or medical equipment failures. Many homeowners mistakenly believe they can simply “plug in” a generator as a weekend DIY project. The harsh reality? Connecting a generator to your house involves navigating 240-volt electrical panels and pressurized gas lines that demand professional expertise. This guide reveals exactly why licensed installation is non-negotiable and what the process actually entails so you can make informed decisions about protecting your family.
Why DIY Generator Installation Puts Your Family at Risk
Electrocution and Fire Hazards You Can’t See
Attempting to connect a generator directly to your home’s electrical system without proper equipment creates deadly backfeed situations. When you improperly wire a generator into your main panel, electricity flows backward through utility lines—energizing downed power lines that repair crews assume are safe. This invisible threat has caused multiple documented fatalities among utility workers during outage restoration efforts. Even experienced handymen lack the specialized training to safely isolate circuits and install transfer switches that meet National Electrical Code requirements.
Critical mistakes that cause disasters:
– Using “suicide cords” that bypass safety mechanisms
– Overlooking proper grounding requirements
– Mismatching wire gauges to circuit loads
– Ignoring clearance requirements around electrical components
Gas Line Dangers That Could Destroy Your Home
Natural gas generator connections require precision that exceeds typical DIY capabilities. A single improperly sealed joint in a gas line creates an invisible explosion hazard that could level your property. Licensed plumbers use specialized leak detection equipment and follow strict pressure testing protocols that homeowners simply cannot replicate. The terrifying reality? Gas leaks often go undetected until it’s too late—carbon monoxide detectors won’t alert you to explosive gas concentrations before ignition occurs.
Standby Generator Installation: What Professionals Actually Do
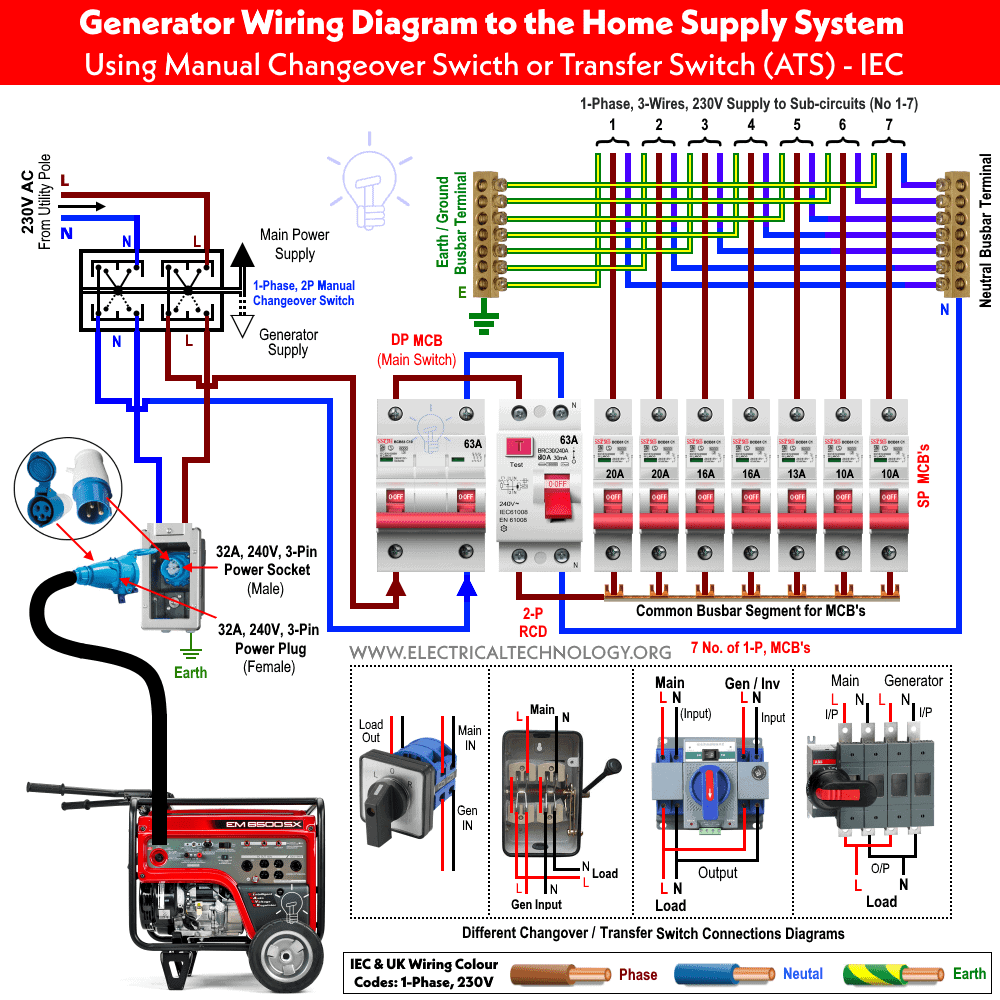
Transfer Switch Installation That Prevents Catastrophe
Licensed electricians begin by installing a dedicated transfer switch adjacent to your main electrical panel—a critical component that safely isolates your home from the utility grid during outages. This isn’t simply “adding another breaker.” Professionals meticulously calculate your electrical load, then strategically relocate essential circuits (refrigeration, medical equipment, sump pumps) to a sub-panel that receives priority power during outages. The transfer switch automatically disconnects from utility power within 10-30 seconds of an outage, preventing dangerous backfeed while seamlessly transitioning your home to generator power.
What proper transfer switch installation includes:
– Mounting a UL-listed switch rated for your generator’s capacity
– Creating a dedicated sub-panel for critical circuits
– Installing interlocks that physically prevent simultaneous grid/generator connection
– Completing load calculations to avoid circuit overloads
Gas Line Installation That Meets Code Requirements
When connecting natural gas generators, licensed plumbers follow a precise sequence that homeowners cannot safely replicate. They begin by marking all underground utilities before trenching, then install tracer wire alongside new gas lines for future location identification. Professionals use corrosion-resistant piping materials that meet local code requirements, with minimum burial depths that prevent accidental damage. Every joint undergoes rigorous pressure testing with specialized equipment—applying 1.5 times normal operating pressure for extended periods to verify zero leaks before final connection.
Portable Generator Connection Methods That Won’t Kill You
Why Extension Cords Create False Security
Many homeowners mistakenly believe that running extension cords from a portable generator provides adequate backup power. This approach creates multiple hidden dangers: cords dragged through windows create tripping hazards while compromising weather seals, outdoor connections become shock risks during rain, and overloaded cords can overheat inside walls causing concealed fires. Most critically, this method leaves hardwired systems like furnaces, well pumps, and security systems completely powerless during outages—defeating the purpose of having backup power.
Power Transfer Systems: The Safer Portable Option

Professionally installed transfer systems provide portable generators with near-standby functionality without permanent installation. These systems include a manual transfer switch mounted near your electrical panel and an outdoor inlet box where you connect your generator. When power fails, you simply plug in your generator, flip the transfer switch, and critical circuits receive power—without dangerous backfeed risks. Unlike extension cords, this method safely powers hardwired appliances like furnaces and well pumps, making it the only acceptable portable generator solution for whole-house coverage.
Natural Gas Connections for Portable Generators Done Right
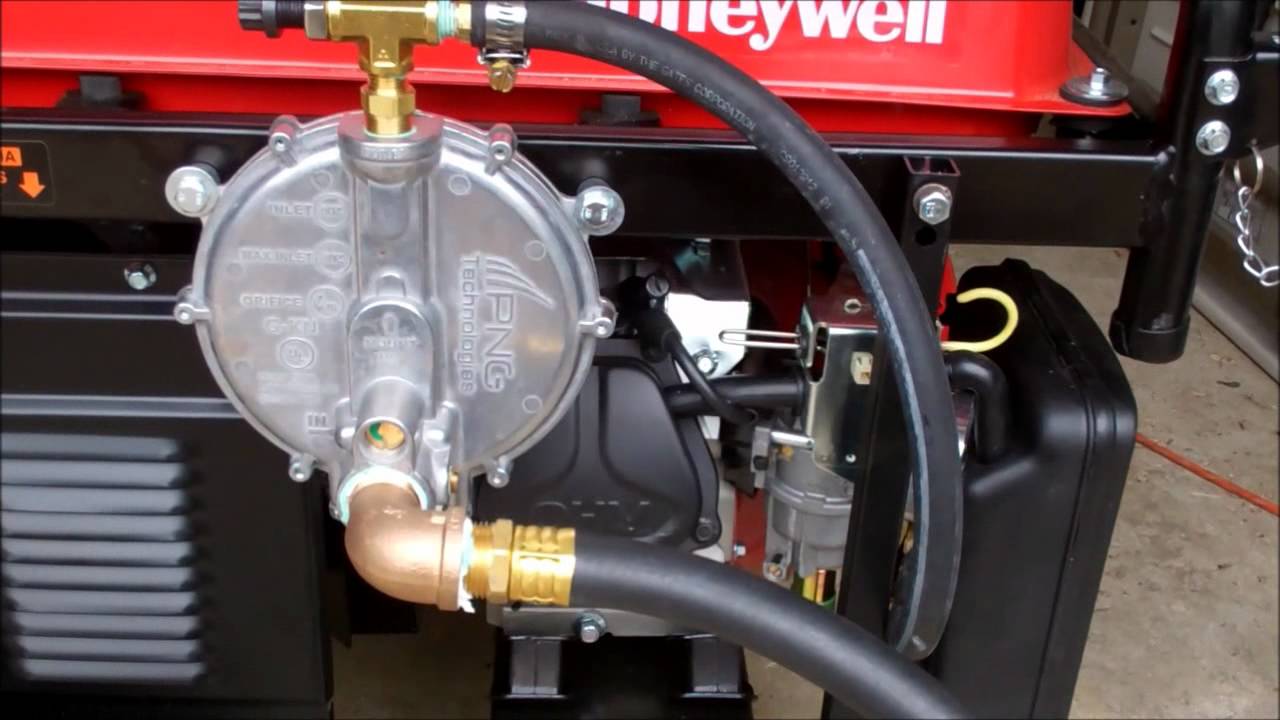
Tri-Fuel Conversion That Requires Professional Gas Work
Adapting your portable generator to run on natural gas eliminates dangerous gasoline storage but demands professional gas line installation. Licensed plumbers create a dedicated branch line after your main gas meter—similar to a gas grill connection but with critical safety upgrades. They install an accessible shutoff valve within 6 feet of the generator, use appropriately sized piping for required BTU flow, and implement proper drip legs to prevent moisture accumulation. Attempting this yourself risks undetected leaks that could fill your generator enclosure with explosive gas before startup.
Professional gas connection requirements:
– Minimum 18-inch clearance from generator exhaust
– Proper slope to prevent condensation traps
– Weatherproof shutoff valve within immediate reach
– Pressure regulators matching generator specifications
Carbon Monoxide Safety Measures That Save Lives
Placement Rules That Prevent Silent Killers
Carbon monoxide poisoning represents the most immediate threat during generator operation—this odorless, colorless gas can incapacitate you in minutes. Professional installers enforce strict placement protocols: generators must sit at least 10 feet from all windows, doors, and vents, with exhaust directed away from building air intakes. They verify airflow patterns around your property to prevent CO recirculation, something most homeowners overlook when placing generators near corners or under eaves. Crucially, they install battery-powered CO detectors on every level of your home—especially near sleeping areas—as your last line of defense.
Warning signs of dangerous CO buildup:
– Generator exhaust visible near building openings
– Unusual wind patterns pushing exhaust toward home
– Snow accumulation around generator exhaust
– Multiple appliances running simultaneously increasing exhaust volume
What Professional Installation Actually Costs
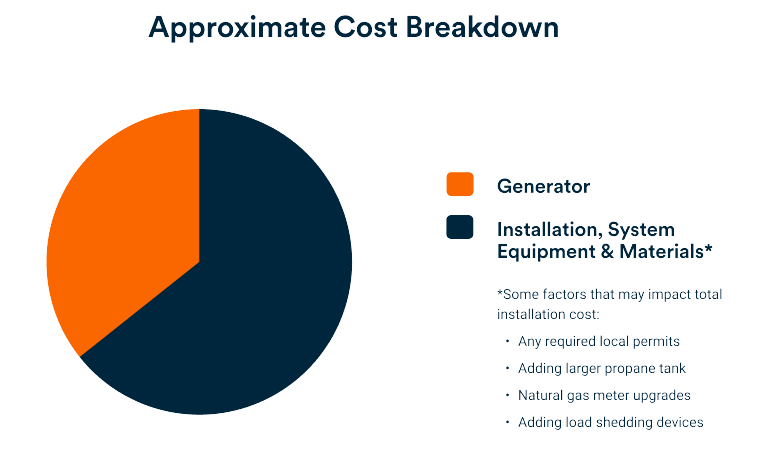
Standby Generator Pricing Breakdown That Prevents Surprise Bills
Most homeowners are shocked to learn that a complete 20,000-watt standby generator installation typically costs $10,000-$15,000—not the $3,000-$5,000 they budget based on generator unit prices alone. This comprehensive cost includes: the generator unit ($4,000-$8,000), transfer switch and electrical work ($2,500-$4,000), gas line installation ($1,500-$2,500), and permit fees ($500-$1,000). Reputable contractors provide detailed itemized quotes showing exactly where your money goes—never accepting full payment until final inspections are passed and the system is fully operational.
Red flags indicating potentially unsafe installation:
– Quotes significantly below market average
– Contractors who don’t pull required permits
– Payment demands for full amount upfront
– No mention of transfer switch specifications
Next Steps That Actually Get Your Generator Installed Safely
Finding Qualified Contractors Who Won’t Cut Corners
Start by verifying electricians hold active master electrician licenses—not just journeyman credentials—and plumbers certified for gas line work. Request proof of current liability insurance ($1 million minimum) and check for specialized generator installation certifications from major manufacturers like Generac or Kohler. The best contractors will provide detailed site assessment reports showing exact generator placement, transfer switch location, and gas line routing before quoting a price. Never hire based solely on price—ask specifically how they handle backfeed prevention and gas line pressure testing.
Essential questions to ask potential installers:
– “Can you show me recent transfer switch installations you’ve completed?”
– “What specific brand and model transfer switch do you recommend for my electrical panel?”
– “How do you verify gas line integrity before final connection?”
– “Will you handle all permit acquisition and scheduling inspections?”
Your family’s safety during the next major outage depends entirely on getting generator installation right the first time. While the investment seems significant, professional installation transforms your backup power from a potential hazard into reliable protection—ensuring your lights stay on without risking your home or your neighbors’ lives. When the next storm hits, you’ll have peace of mind knowing your generator operates exactly as designed, with zero compromise on safety protocols that protect everyone involved.