Your generator faces its toughest challenge during summer heat waves when you need reliable power most. When ambient temperatures climb past 104°F (40°C), your generator begins silently losing power capacity—exactly when air conditioning and other critical systems demand maximum electricity. Without proper cooling strategies, your generator could fail when you depend on it most, leaving you in sweltering darkness during a power outage.
Heat is your generator’s invisible enemy, degrading performance long before complete failure. The good news? Implementing these cooling techniques ensures your generator delivers full power even during brutal heat. This guide reveals the exact maintenance routines and modifications professionals use to maintain peak generator performance when temperatures threaten to shut you down.
Why Your Generator Loses Power at 104°F Ambient Temperature
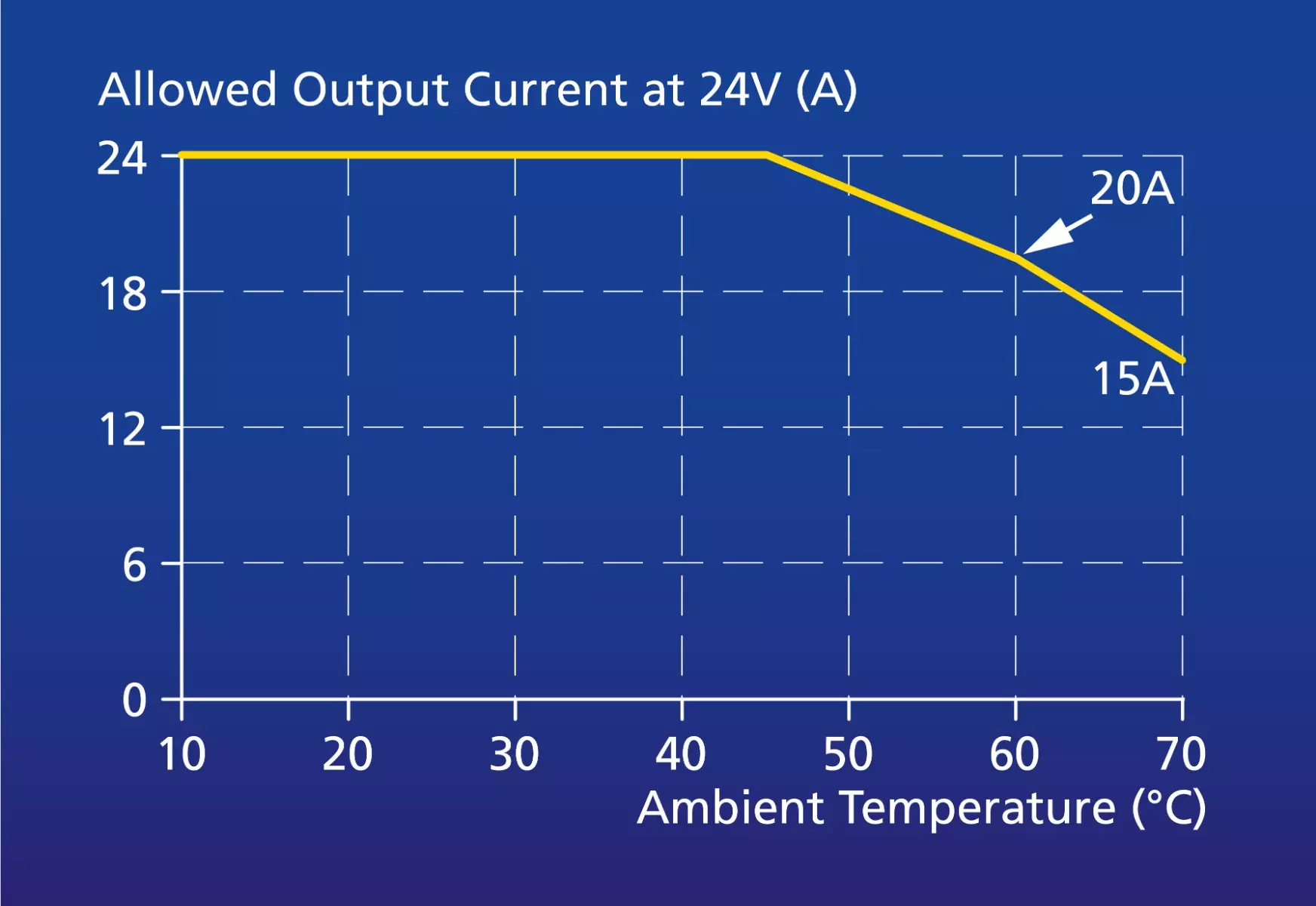
Generators hit a critical tipping point at 104°F ambient temperature. Beyond this threshold, manufacturers require immediate derating—reducing power output to prevent thermal damage. This isn’t optional; it’s a built-in safety mechanism that protects your investment from catastrophic failure.
Each degree above 104°F forces additional power reduction. A 20kW generator might drop to 16kW output at 110°F, potentially leaving critical circuits underpowered. Understanding this relationship helps you anticipate power shortages during heat waves and adjust your load requirements accordingly.
Daily Coolant and Oil Checks That Prevent Overheating
Check coolant levels every morning during hot weather operation. Low coolant is the fastest path to overheating failure. Locate your coolant reservoir and verify levels fall between minimum and maximum marks—never overfill, as expansion requires space.
Use only manufacturer-specified coolant type. Generic antifreeze creates chemical reactions that reduce heat transfer efficiency. The standard 50/50 antifreeze-to-water ratio provides optimal boiling point elevation while maintaining freeze protection for year-round reliability.
Monitor oil quality daily during extreme heat. Healthy oil transforms from amber to black as thermal breakdown occurs, losing viscosity and heat-carrying capacity. Maintain oil at maximum safe level without overfilling. Replace immediately if the oil feels watery between your fingers or darkens significantly.
Air Filter Maintenance That Stops Heat Buildup Before It Starts
Dirty air filters force your generator to work harder, generating unnecessary heat. Inspect filters every 50 operating hours or weekly during dusty summer conditions. Restricted airflow from clogged filters directly contributes to overheating problems.
Effective air filter cleaning:
– Remove filter and gently tap against hard surface
– Use compressed air from clean side outward
– Replace immediately if tears appear or dirt won’t dislodge
Warning signs you’ve waited too long:
– Noticeable reduction in engine performance
– Increased fuel consumption without load changes
– Higher operating temperatures than normal
Radiator Fin Cleaning That Restores Cooling Efficiency
Radiator fins clogged with debris act like a wool blanket wrapped around your generator. Grass, leaves, and insects accumulate in fin gaps, dramatically reducing heat dissipation. Use compressed air or a leaf blower to clear debris weekly during summer heat.
Never use water or solvents on the radiator—moisture causes rapid corrosion and bearing contamination. Clean from multiple angles, expecting substantial dust expulsion. Focus on areas where environmental debris accumulates most heavily for maximum cooling improvement.
Generator Shade Solutions That Cut Surface Temperature by 20°F

Direct sunlight adds 15-20°F to generator surface temperature, pushing already stressed components closer to failure. Install temporary shade structures using UV-resistant tarps mounted on poles at least 3 feet from the generator. Ensure adequate airflow around the unit while blocking direct sun exposure.
Position generators on the north side of buildings when possible, as this area remains cooler throughout the day. Even simple shade solutions dramatically reduce cooling system load. For permanent installations, consider prefabricated generator enclosures with proper ventilation designed specifically for high-temperature operation.
Strategic Site Selection for Naturally Cooler Operation
Choose naturally cooler locations on your property to give your generator the best chance during heat waves. Look for areas with consistent breeze exposure—moving air significantly enhances cooling efficiency. Low-lying spots work well since cold air settles in these areas.
Place generators on concrete or other reflective surfaces rather than asphalt, which radiates additional heat. Maintain at least 5 feet clearance on all sides for permanent installations, increasing clearance when ambient temperatures exceed 95°F. These small temperature differentials of just 5-10°F dramatically reduce cooling system stress.
Smart Load Management That Prevents Thermal Shutdown
Never exceed continuous rating during extreme heat. Your generator’s standby rating is for temporary use only—continuous operation above the continuous rating generates dangerous heat levels. During peak heat, prioritize essential circuits and rotate non-critical loads every 2-3 hours.
Effective load distribution:
– Schedule high-draw appliances at different times
– Allow 15-minute cool-down periods after 4 hours above 75% load
– Monitor temperature continuously during high-load operation
Install priority-based load disconnection systems that automatically reduce power draw when temperatures approach limits. These systems prevent thermal shutdown by disconnecting non-essential equipment before damage occurs. Manual protocols work too—establish predetermined load reduction sequences for high-temperature days.
Battery Cooling Techniques That Prevent Starting Failures
Heat accelerates electrolyte evaporation, causing starting failures when you need power most. Check battery fluid levels weekly during hot weather, adding distilled water to cover plates when levels drop. Clean terminals with a brass brush to remove oxides, then apply protective grease to prevent corrosion.
Battery cooling checklist:
– Ensure battery compartment has adequate ventilation
– Position batteries away from direct engine heat
– Apply dielectric grease to terminals after cleaning
– Keep batteries clean and dry to prevent parasitic discharge
Hot batteries produce more hydrogen gas, increasing corrosion risk. This simple maintenance prevents power-robbing resistance that generates additional heat at critical connection points.
Emergency Overheating Response That Saves Your Generator

When overheating occurs, quick action prevents catastrophic damage. Gradually reduce electrical load over 30-60 seconds to prevent voltage spikes. Allow the engine to idle 3-5 minutes for thermal equalization before complete shutdown.
Wait at least 30 minutes before checking coolant—opening a hot system risks severe burns. Inspect for visible leaks or component damage, and document ambient temperature and load conditions for future analysis. Never restart immediately after overheating; allow minimum 1-hour cool-down for complete thermal recovery.
Temperature Monitoring That Catches Problems Early
Maintain hourly temperature logs during hot weather operation. Record ambient temperature, coolant temperature, and oil pressure to identify developing problems before failures occur. Install temperature gauges at radiator inlet and outlet to monitor cooling system effectiveness—healthy systems show a 15°F differential.
Critical thresholds requiring immediate action:
– Coolant temperature above 220°F: Reduce load immediately
– Oil pressure below 30 PSI at operating temperature: Shut down
– Ambient temperature approaching 104°F: Begin derating calculations
Professional Maintenance That Maximizes Summer Reliability
Schedule professional thermal imaging of electrical connections annually during summer months. Hot spots invisible to the eye indicate failing connections that generate excessive heat throughout the system. Critical applications require biannual service, especially before peak summer demand.
Coolant and oil systems need professional flushing every 150 hours or 3 months during high-temperature operation. Contaminated fluids lose heat transfer capability, creating dangerous operating conditions that lead to premature failure.
Key Takeaway: Generator cooling isn’t optional summer maintenance—it’s your insurance against power failure when you need electricity most. The 15 minutes spent on daily checks prevents days without power and thousands in repair costs. Start with proper shade and filter maintenance today, then implement advanced cooling strategies before the next heat wave strikes your area. Your future self will thank you when the temperature soars but your generator keeps delivering reliable power.