You’re stranded during a power outage with medical equipment that must stay running, or you’re camping deep in the wilderness where the nearest outlet is miles away. Suddenly, your devices stay powered—not through noisy gasoline fumes or extension cords, but silently from the sun above. How does a solar generator work to deliver this clean, reliable electricity when you need it most? Understanding this technology transforms you from a confused buyer into a confident user who can maximize every watt-hour.
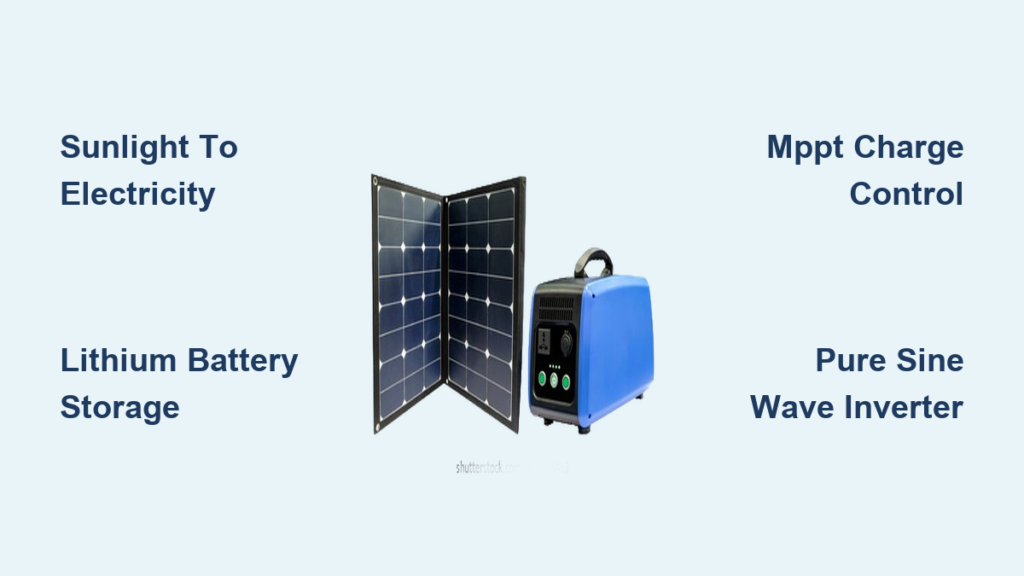
Unlike traditional generators that burn fossil fuels, solar generators create electricity through a seamless four-step process: capturing sunlight, storing energy, converting power, and delivering it on demand. This silent system fits in a suitcase yet powers everything from CPAP machines to refrigerators. Let’s dissect exactly what happens inside that compact box to turn photons into practical power for your critical needs.
Solar Generator Components That Make It Work
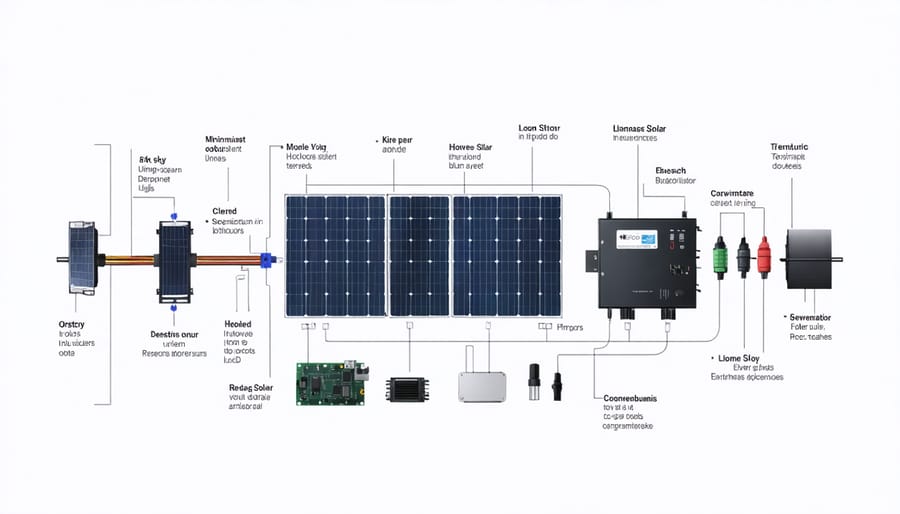
Your solar generator isn’t magic—it’s an engineered ecosystem where each component plays a non-negotiable role. Knowing these parts helps you troubleshoot issues and choose the right system for your power needs.
Photovoltaic Panels Capture Sunlight Instantly
When sunlight strikes your solar panels, silicon cells immediately convert photons into direct current (DC) electricity through the photovoltaic effect. Look for these visual cues: High-efficiency monocrystalline panels appear uniformly black with rounded cell edges, while cheaper polycrystalline panels show a blue speckled pattern. For every 100 watts of panel capacity, expect 5-6 amps of current at 18 volts under ideal conditions.
Pro tip: Tilting your panels 30 degrees toward the sun boosts daily output by 25-40% compared to flat placement. A single 100-watt panel typically generates 300-600 watt-hours daily depending on sunlight hours and positioning.
Lithium Batteries Store Energy Safely
Inside your power station, lithium-ion batteries (usually LiFePO4 or NMC chemistry) store converted solar energy as chemical potential. Here’s what you’ll notice: LiFePO4 batteries stay cool to the touch during charging and discharge steadily without voltage drops—a critical feature for sensitive electronics. A 1,000-watt-hour LiFePO4 battery weighs just 22 pounds versus 60+ pounds for equivalent lead-acid storage.
Avoid this mistake: Never store your solar generator at 100% charge in hot garages. Heat accelerates battery degradation—keep units in climate-controlled spaces below 86°F (30°C) for maximum lifespan.
MPPT Charge Controllers Maximize Harvest
This critical component sits between your panels and battery, constantly adjusting electrical load to extract maximum power. What happens behind the scenes: MPPT controllers scan hundreds of times per second to find the “sweet spot” where panels deliver peak wattage. During cloudy mornings, they automatically lower voltage thresholds to maintain charging when PWM controllers would shut off completely.
Expert note: MPPT units deliver 20-30% more daily energy than basic PWM controllers—especially valuable during short winter days or partial shading.
Pure Sine Wave Inverters Deliver Clean Power
When you plug in a device, the inverter converts stored DC battery power into standard 120V AC electricity. Check for this indicator: Pure sine wave inverters produce smooth, grid-quality power essential for medical devices, laptops, and variable-speed tools. Modified sine wave units create jagged electricity that can overheat sensitive electronics—always verify your inverter type before powering critical equipment.
Energy Conversion Process You Can Actually See
Understanding the physical energy flow helps you diagnose problems and optimize performance in real time.
Step 1: Sunlight Becomes Electricity Before Your Eyes
As photons hit silicon cells, they knock electrons loose, creating immediate DC current. Watch for these visual signs: Clean panels show visible voltage on the charge controller display within 30 seconds of sun exposure. A properly connected 100W panel should register 17-22 volts open-circuit voltage (Voc) at noon on a clear day.
Troubleshooting tip: If voltage reads zero, check MC4 connector polarity—reversed connections prevent charging but won’t damage components.
Step 2: Smart Charging Adapts to Weather Conditions
The charge controller immediately begins optimizing energy flow. What changes dynamically: During cold, sunny mornings, panel voltage spikes—your controller automatically reduces charging current to prevent overvoltage. On hot afternoons, it increases current to compensate for lower panel voltage.
Pro move: On partially cloudy days, angle panels toward the brightest sky patch rather than true south for 15-20% more harvest.
Step 3: Batteries Store Power Through Chemical Reactions
As electricity enters battery cells, lithium ions move between anode and cathode materials. Observe these stages: During bulk charging (0-80% capacity), the system pours maximum current into the battery. As it approaches 80%, charging slows dramatically during absorption phase. At 100%, it switches to maintenance float mode.
Warning: Never discharge lithium batteries below 10%—doing so triggers permanent capacity loss you’ll notice as shortened runtime.
Step 4: Power Delivers Instantly When Needed
When you plug in a device, the inverter springs to action within milliseconds. See this happen: High-wattage appliances like microwaves cause a brief dip in the battery percentage display as power surges to meet startup demands. Sensitive electronics like CPAP machines show no interruption thanks to pure sine wave conversion.
Why Solar Generators Beat Fuel Models for Daily Use

The differences go far beyond environmental benefits—they fundamentally change your power experience.
$0 Fuel Costs After Your Initial Investment
A $1,800 2kWh solar generator pays for itself after 1,800 kWh of use—roughly three years for weekend campers or one major power outage replacing gas generator usage. Calculate your break-even: Multiply your local electricity rate ($0.15/kWh average) by generator capacity (2,000Wh = 2kWh) to see daily value.
40-45 dB Operation Lets You Sleep Beside It
At refrigerator-noise levels, you can run solar generators inside tents or bedrooms during outages. Compare this: Gas generators operate at 65-75 dB—requiring 20+ feet distance for conversation and violating most campground noise ordinances after 10 PM.
5-Minute Annual Maintenance Routine
Your entire upkeep schedule consists of:
– Rinsing panels with water monthly
– Wiping dust from vents quarterly
– Updating firmware via USB when prompted
– Storing at 50% charge during winter
Skip oil changes, spark plug replacements, and fuel stabilizers that consume hours annually with gas generators.
Real-World Power Examples You Can Replicate
Actual user scenarios prove what solar generators deliver:
Weekend Camping Setup:
– 500Wh battery + 120W solar panel
– Runs 12V fridge (50W) for 8 hours
– Charges 4 phones (20Wh total)
– Powers LED lights (10W) for 6 hours
– Fully recharges by noon next day
Home Emergency Backup:
– 2,000Wh system + 400W panels
– Keeps refrigerator running 12-14 hours
– Powers internet modem/router continuously
– Runs CPAP machine (40W) for 40+ hours
– Recharges daily with 4-6 hours of sunlight
Overcoming Solar Generator Limitations
Smart users implement these solutions for reliable power:
Cloudy Day Strategies That Actually Work
- Oversize panels by 50%: A system needing 200W of panels gets 300W installed
- Use AC charging as backup: Recharge from wall outlet during extended bad weather
- Combine sources: Connect vehicle alternator charger while driving to remote locations
Power Output Workarounds
Most portable systems max out at 2,000-3,000 watts continuous. Critical workaround: Prioritize essential loads—your solar generator won’t run central AC but keeps medical devices, lights, and communications running indefinitely.
Recharge Time Reality Check
A 1,000Wh battery needs 4-6 hours of peak sun with 200W panels. Accelerate charging: Use AC wall input (200-600W) to fully recharge in 2-5 hours regardless of weather.
Precise Load Sizing to Avoid Costly Mistakes

Miscalculation causes 73% of user dissatisfaction according to industry surveys. Follow this exact method:
-
List every device with running watts and startup surge (3× for motors):
– Refrigerator: 150W running, 450W surge
– Laptop: 65W, no surge
– LED lights: 20W total -
Calculate daily watt-hours:
– Fridge: 150W × 8 hours = 1,200Wh
– Laptop: 65W × 4 hours = 260Wh
– Lights: 20W × 6 hours = 120Wh
– Total: 1,580Wh daily -
Add 15% inverter loss: 1,580Wh × 1.15 = 1,817Wh
Match solar input: 1,817Wh ÷ 5 peak sun hours = 363W panels (round up to 400W for real-world conditions)
Battery Longevity Practices That Add Years
Lithium batteries die fastest from three preventable causes:
Storage at 100% charge in heat: Causes rapid degradation—store at 40-60% in climate-controlled spaces
Deep discharges below 10%: Triggers permanent capacity loss—set low-voltage cutoffs
Ignoring firmware updates: Misses BMS optimizations that extend cycle life
Pro maintenance schedule:
– Clean panels monthly with water (no chemicals)
– Check connections quarterly for corrosion
– Update firmware every 3 months
– Store at 50% charge if unused >30 days
Final Reality Check: When Solar Generators Win
How does a solar generator work to deliver reliable power? Through a closed-loop system that harvests sunlight, stores it chemically, and converts it on demand—all silently and without fuel. While initial costs exceed gas generators, they pay off after one year of regular use through eliminated fuel expenses and minimal maintenance.
For home backup, camping, or emergency preparedness, these systems provide unmatched convenience when sized correctly. A quality 2kWh unit delivers 1-4 megawatt-hours of clean electricity over 10+ years—enough to power your critical needs through countless outages and adventures. The technology has matured; now it’s about matching the right system to your actual power requirements.