When wind rushes through your local wind farm, those massive spinning blades are performing a remarkable transformation you might not fully appreciate. How does a wind generator work to convert that invisible air movement into the electricity powering your home? The answer lies in a precisely engineered sequence that transforms kinetic energy into electrical energy through aerodynamics, mechanical systems, and electromagnetic principles. Understanding this process reveals why wind power has become one of the most rapidly expanding renewable energy sources worldwide.
From the moment wind contacts the turbine blades to when electricity flows into your home, multiple sophisticated systems work in concert within seconds. You’re about to discover the exact mechanisms that make this clean energy conversion possible—and how modern engineering has optimized every step of the process.
Why Wind Turbine Blades Spin Using Aerodynamic Lift
Airfoil Design Creates Rotational Force
Wind generator blades function similarly to airplane wings but with a crucial difference in application. The curved upper surface accelerates airflow, creating lower pressure above the blade compared to the flatter lower surface. This pressure differential generates lift force perpendicular to wind direction, causing the blade to rotate around the central hub. Modern three-blade rotors maximize this effect through carefully engineered airfoil cross-sections that optimize the lift-to-drag ratio for efficient energy extraction.
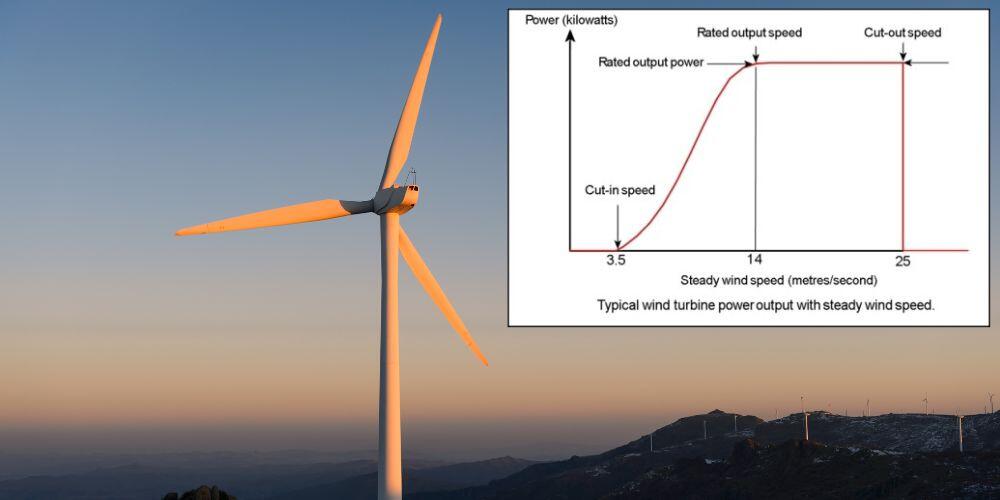
Critical Wind Speed Thresholds Determine Operation
Wind generators don’t operate across all wind conditions—they require specific velocity ranges to function safely and efficiently:
- Cut-in speed: 6.2 mph (10 km/h) minimum for power generation to begin
- Rated speed: Optimal wind velocity for maximum power output (varies by model)
- Cut-out speed: 56 mph (90 km/h) triggers automatic shutdown for safety
Between these thresholds, your wind generator continuously adjusts blade angles to extract maximum energy while protecting equipment from damage. When wind speeds fall below cut-in speed, the generator stops producing electricity, while exceeding cut-out speed activates safety protocols to prevent mechanical stress.
Gearbox Transformation: From Slow Spin to Electricity Generation

Rotor Assembly Mechanics Convert Wind Force
The three-blade rotor assembly converts aerodynamic force into rotational mechanical energy. Despite their enormous size—with sweeping areas exceeding that of a football field—these rotors spin relatively slowly, typically 18-25 RPM under normal conditions. This gentle rotation presents a significant challenge: electric generators require much higher speeds to produce electricity efficiently.
Speed Multiplication Through Precision Engineering
The gearbox serves as the mechanical heart of your wind generator, solving the speed mismatch problem. This complex system increases rotational speed by approximately 72 times, transforming the rotor’s 25 RPM spin into the generator’s required 1,800 RPM. Inside the gearbox, planetary gears and parallel shaft arrangements distribute enormous torque loads across multiple gear stages while maintaining efficiency above 95%. Advanced lubrication systems ensure smooth operation under extreme loads and temperature variations that your wind generator encounters daily.
Electromagnetic Conversion: From Mechanical Rotation to Electrical Current
Generator Creates Electricity Through Magnetic Fields
How does a wind generator work to produce actual electricity? The high-speed shaft from the gearbox connects directly to the generator, where mechanical energy becomes electrical energy through electromagnetic induction. Inside the generator, powerful rare-earth magnets rotate past copper coil windings, creating alternating current (AC) electricity. This process follows Faraday’s law of induction—when a conductor moves through a magnetic field, it generates electrical current.
Power Conditioning Ensures Grid Compatibility
Raw generator output requires significant conditioning before connecting to your home’s electrical grid. Transformers within the nacelle perform three critical functions:
- Voltage elevation: Increases from 690V generator output to 20-35 kV transmission levels
- Frequency matching: Ensures perfect synchronization with grid requirements (60 Hz in North America)
- Electrical isolation: Provides safety separation between generator and grid systems
Additional power electronics smooth voltage fluctuations to ensure consistent power quality regardless of wind variability, making the electricity from your wind generator indistinguishable from conventional sources.
Intelligent Control Systems That Keep Wind Generators Running Safely

Nacelle Technology Manages Wind Direction and Power Output
The nacelle—housing all operational systems—functions as your wind generator’s sophisticated control center. Key systems include:
- Yaw system: Automatically rotates the entire nacelle to track wind direction using wind vane sensors
- Pitch control: Individual blade angle adjustment optimizes power capture and provides emergency braking
- Monitoring systems: Continuous tracking of wind speed, vibration, temperature, and power output
These systems work together to maximize energy capture while protecting your investment from damage during extreme conditions.
Automatic Safety Protocols Prevent Equipment Damage
Modern wind generators operate autonomously while maintaining strict safety protocols:
- Wind monitoring: Automatic shutdown occurs when speeds exceed 56 mph
- Lightning protection: Integrated systems in blade design and tower grounding
- Ice detection: Sensors identify blade ice accumulation, triggering shutdown protocols
- Fire suppression: Automatic systems within the nacelle protect against electrical fires
These systems operate continuously, often preventing damage before you even know a problem exists, ensuring your wind generator operates safely for decades.
Wind Farm Integration That Powers Entire Communities
Electrical Collection Systems Balance Multiple Turbines
Individual wind generators connect through underground cables to a central collection system. Each turbine feeds into common transformer substations that step up voltage for long-distance transmission. This network operates like a miniature electrical grid, managing power flow from dozens or hundreds of turbines simultaneously.
The collection system automatically balances power fluctuations. When one wind generator experiences reduced wind, others compensate through the interconnected system, maintaining consistent power delivery to your main electrical grid despite changing wind conditions.
Smart Grid Integration Enhances Renewable Energy Value
Advanced wind farms communicate directly with grid operators, providing real-time generation data. This two-way communication enables wind generators to participate in grid stabilization, reducing output during excess supply or ramping up during peak demand periods. Understanding how a wind generator works reveals its sophisticated role in modern energy infrastructure beyond simple electricity production.
Performance Metrics That Demonstrate Wind Power Effectiveness
Real-World Energy Production Capabilities
Contemporary wind technology delivers substantial power to your community:
- Single turbine capacity: Powers 400-600 average homes
- Capacity factors: Modern turbines achieve 35-45% efficiency
- Height advantage: Taller towers access stronger, more consistent winds at 300+ feet elevation
- Grid contribution: Wind provided 10.3% of U.S. utility-scale electricity in 2022
These metrics show why wind generators have become such a critical component of clean energy strategies worldwide.
Continuous Technology Improvements Drive Better Performance
Ongoing innovation enhances wind generator capabilities:
- Blade aerodynamics: Computational fluid dynamics optimize blade shapes for specific wind regimes
- Generator efficiency: Advanced magnet designs exceed 95% conversion efficiency
- Predictive maintenance: AI-powered monitoring prevents failures and extends operational life
- Grid integration: Enhanced power electronics enable seamless renewable energy connection
These advancements make understanding how a wind generator works increasingly important as technology evolves.
Environmental and Economic Benefits of Wind Energy
Clean Power Generation Without Emissions
Wind generators produce zero operational emissions while generating substantial electricity. A single 2.5 MW turbine prevents approximately 4,000 tons of CO2 emissions annually compared to fossil fuel generation. The renewable nature ensures sustainable energy production without depleting resources that future generations will need.
Significant Economic Impact for Communities
Wind energy creates substantial economic value:
- Job creation: Over 140,000 U.S. wind industry jobs as of 2023
- Land use efficiency: Farmers receive lease payments while continuing agricultural operations
- Cost reduction: Wind electricity costs decreased 69% between 2009-2022
- Energy independence: Reduces reliance on imported fossil fuels
Understanding how a wind generator works reveals not just the technical process but also its broader societal benefits.
Wind generators represent sophisticated engineering achievements that transform nature’s most abundant resource—moving air—into clean, reliable electricity. The precise sequence from aerodynamic blade design to electrical grid synchronization demonstrates why wind power has become such a rapidly growing energy source. As you now understand how a wind generator works, you can appreciate the remarkable technology converting invisible air movement into the electricity powering your daily life. Each time you see those massive blades spinning, remember the complex energy transformation happening within that towering structure.