Your diesel generator sat idle for months, then failed when you needed it most—a storm’s approaching, the lights flicker, and that ominous clicking sound means no power. This diesel generator troubleshooting guide delivers field-tested solutions from technicians who fix 5 kW home units to 150 kW commercial systems. You’ll diagnose problems in minutes, not hours, with actionable steps that prevent panic during outages.
Stop guessing why your generator won’t start or loses power under load. We’ve condensed critical diagnostics into symptom-specific sections so you can match your issue to precise fixes. Every procedure here comes from real-world service data, not theory. By the end, you’ll know exactly how to test battery health, clear fuel system blockages, and spot dangerous overheating signs before they cause catastrophic failure.
Immediate Symptom Response Protocol
Won’t Crank or Clicking Noise Only
Check your battery voltage first—anything below 12.6V means you’re fighting a losing battle. A fully charged battery should maintain at least 9.6V during cranking. Clean corroded terminals with a wire brush and baking soda solution, then retest. If voltage still drops, your battery needs replacement, not just charging.
Test the starter circuit by measuring voltage drop from battery positive to starter positive while cranking. Anything over 0.5V indicates dangerous resistance in cables or connections. Listen for a single loud click—that’s your solenoid engaging but the starter motor failing. Bench-test the starter: healthy units draw under 80A on 5-7kW generators. Replace worn brushes if they’re shorter than 1/4 inch.
Cranks But Won’t Start
Fuel starvation causes 70% of no-start issues after long storage. Confirm fuel level exceeds 1/4 tank—diesel pickup tubes sit higher than gasoline units to avoid sediment. Hand-prime the lift pump until resistance firms up within 10 strokes. Crack the injector line at cylinder #1 while cranking; you should see steady fuel spurts. No fuel flow? You’ve got air in the system or a clogged primary filter.
Check glow plugs on cold mornings—they should draw 15-25A total with individual resistance between 0.5-2.0Ω. Weak plugs cause hard starting and white smoke. Replace any glow plug drawing more than 30% less current than others. Never skip this check below 50°F ambient temperature.
Black Smoke Under Load Diagnosis

Air Intake Restrictions
A clogged air filter chokes your generator, causing incomplete combustion and black smoke. Check restriction gauges—if they read over 25 inches of water column, replace immediately. Visually inspect pleats; if 50% appear dirty, don’t wait. A $20 filter prevents $2,000 injector repairs. Clean reusable filters with compressed air from the clean side outward at 30 PSI max.
Faulty Fuel Injectors
Perform a leak-off test by collecting return fuel from each injector for one minute at idle. Healthy units return 45-60ml—excess indicates worn nozzles dumping too much fuel. Spray pattern matters more than flow rate; inspect with a stethoscope while running. Proper spray forms a fine cone without drips or streams. Replace injectors showing uneven patterns.
Turbocharger Performance Check
Measure boost pressure at full load with a mechanical gauge—most 50kW units need 15-20 PSI. Low boost means your turbo isn’t spooling properly. Inspect compressor wheel for oil residue (indicates seal failure) or blade damage. Check backpressure at the turbo outlet—it must stay under 2 PSI at rated load. Excessive backpressure points to a clogged exhaust system.
Overheating Emergency Fixes
Coolant System Verification
Cold coolant levels must sit between MIN and MAX marks—never top off a hot system. Pressure test to 15 PSI; a drop exceeding 1 PSI every two minutes means leaks. Add UV dye to pinpoint cracks in hoses or the radiator. Replace any hose showing bulging over 10% of its diameter under pressure.
Radiator Cleaning Protocol
Bent radiator fins reduce cooling efficiency by up to 40%. Straighten them with a specialized fin comb, working from top to bottom. Never use water pressure above 30 PSI—forced air from the engine side outward clears debris without damaging fins. Flush the system with 5% citric acid solution every 500 hours to remove scale buildup.
Thermostat and Water Pump Testing
Remove the thermostat and test in a water bath—it must begin opening at the manufacturer’s specified temperature (typically 180°F/82°C). A stuck-closed thermostat causes instant overheating. Check the water pump weep hole for leaks and shaft play; any movement means imminent failure. Flow test results should match your generator’s specifications—usually 5+ gallons per minute at 1800 RPM.
Voltage Instability Solutions
No Output Recovery
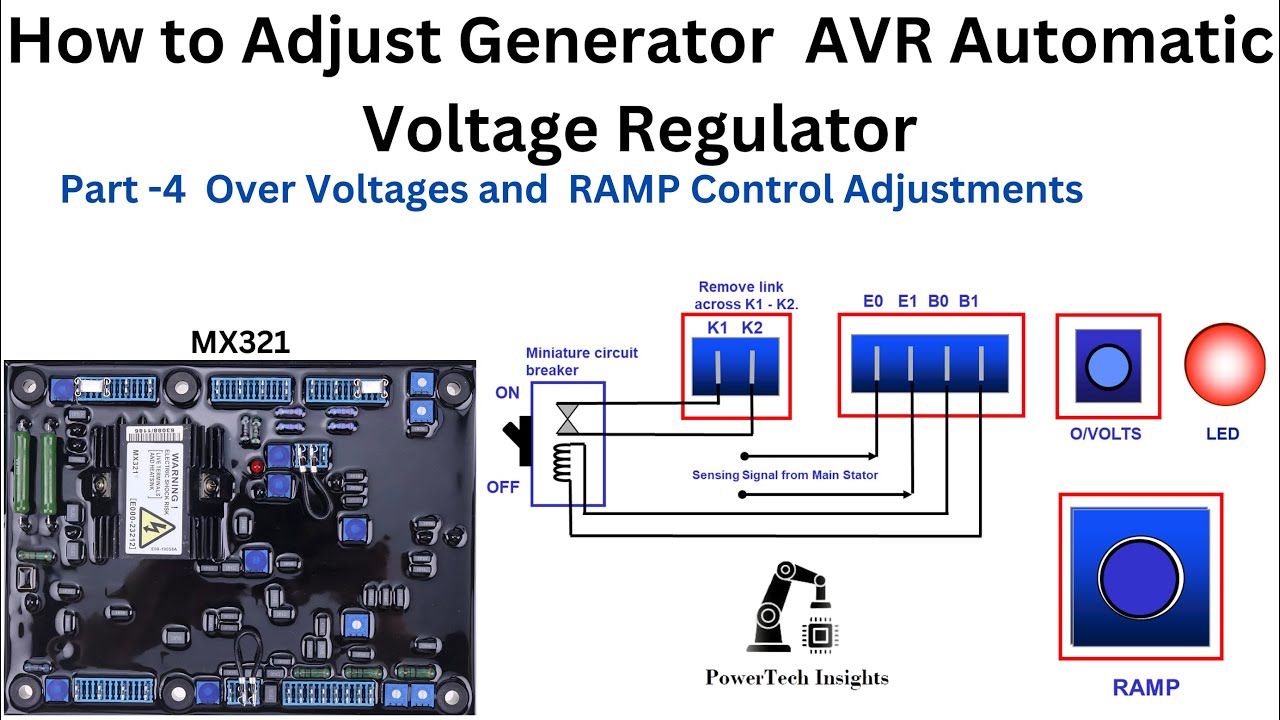
First confirm your excitation fuse hasn’t blown—this small component kills all output. Test for residual magnetism by flashing the rotor leads with a 12V battery for 2-5 seconds. No voltage after flashing? Your AVR (Automatic Voltage Regulator) has likely failed. Check sensing leads for loose connections—they must read at least 190V on a 240V system.
Fluctuating Voltage Correction
Adjust the AVR’s stability potentiometer in 1% increments while monitoring voltage under 25% load. Excessive fluctuations often trace to a failing diode trio—measure resistance across diodes; readings should match between 0.3-0.7Ω. Replace the entire trio rather than individual diodes. Verify belt tension at 30-50 pounds—slippage causes immediate voltage drops during load changes.
Preventive Maintenance That Prevents Emergencies

Critical 6-Month Service Checklist
Change engine oil and filter every 100-150 hours or six months—whichever comes first. Use API CK-4 15W-40 diesel-specific oil that handles soot better than standard motor oil. Replace both primary and secondary fuel filters annually, even if hours are low—stale diesel forms gum that clogs systems. Load bank test your generator yearly for 30 minutes at 80% capacity to burn off carbon deposits.
Emergency Preparedness Kit Essentials
Store double your estimated daily fuel consumption as reserve—add biocide to prevent microbial growth. Keep 5 liters of oil, 2 liters of coolant concentrate, spare filters, and belts in a sealed container. Include a laminated wiring diagram and technician hotline number taped inside the enclosure. Test battery connections monthly with a load tester—corrosion causes 40% of unexpected failures.
When to Stop DIY and Call a Professional
Replace components only when you can verify the problem through testing. Call a certified technician immediately if you detect internal knocking sounds or find metal particles in the oil—these indicate catastrophic engine damage. Significant crankshaft runout (>0.003 inches) requires specialized equipment to measure and correct. Electrical faults like stator insulation below 1 MΩ at 500V DC demand professional testing gear.
Never attempt turbocharger repairs if shaft play exceeds 0.020 inches radial—improper balancing creates dangerous vibrations. Repeated safety shutdowns after fixes suggest deeper issues beyond amateur diagnosis. Professional service pays for itself when preventing a $10,000 engine rebuild from improper troubleshooting.
Keep this diesel generator troubleshooting guide in your maintenance tote alongside your emergency kit. Next time your generator stumbles, you’ll diagnose the problem in minutes, implement proven fixes, and maintain power through any outage. Proper care extends generator life by 30% according to DoE data—your investment in these procedures returns reliable power when the grid fails.