Carbon monoxide poisoning from generators kills hundreds every year, often striking families during power outages when they desperately need backup power. This invisible threat claims victims silently—within minutes of exposure—leaving survivors with permanent heart and brain damage. The tragedy? These deaths are entirely preventable with proper safety measures.
During emergency situations like hurricanes or winter storms, generator safety becomes crucial. A single mistake—running your generator in the garage with the door open—can turn your safety device into a deadly weapon. This guide walks you through proven strategies to protect your family while maintaining essential power during outages. You’ll learn exactly where to position your generator, what safety equipment you need immediately, and the emergency protocols that could save your life when seconds count.
Never Run Your Generator Inside Any Enclosed Space
Operating a generator indoors creates a lethal carbon monoxide trap that can kill within minutes. This isn’t a warning to take lightly—following the November 2011 snowstorm in Connecticut, carbon monoxide poisoning accounted for 18% of all storm-related deaths. The U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission now mandates explicit warning labels on all portable generators stating: “Using a generator indoors CAN KILL YOU IN MINUTES.”
Critical Locations That Create Deadly CO Buildup
- Your garage—even with the door wide open—allows carbon monoxide to seep into your home
- Basements and crawl spaces—these below-grade areas trap exhaust gases at dangerous concentrations
- Under porches or carports—these partially covered areas create perfect conditions for CO accumulation
- Near open windows—wind patterns can easily draw exhaust into your living spaces
Many people mistakenly believe that cracking a window or operating in a “well-ventilated” garage provides adequate protection. This dangerous misconception kills people every year. Carbon monoxide from generators builds up faster than you can detect it—often before you notice symptoms.
Position Your Generator at Minimum Safe Distances

Proper generator placement creates the critical barrier between your family and carbon monoxide poisoning. Distance and positioning determine whether exhaust gases drift harmlessly away or silently infiltrate your home.
Exact Placement Measurements That Save Lives
- 20-foot minimum rule—position your generator at least 20 feet from all doors, windows, and vents (this is the gold standard recommended by safety experts)
- 10-foot absolute minimum—only use this reduced distance when space constraints make 20 feet impossible, and even then, monitor wind patterns carefully
- Exhaust direction matters—always point the generator’s exhaust away from your home, never toward it
- Wind pattern awareness—position your generator accounting for prevailing wind directions in your area
Safe Weather Protection Methods for Storm Conditions
Power outages often happen during severe weather, creating a dangerous dilemma: you need protection from rain but can’t compromise ventilation. Never use makeshift solutions like tarps or cardboard that restrict airflow.
Use only these approved weather protection options:
– Generator-specific canopies like GenTent that maintain 360-degree ventilation while protecting from rain
– Open-sided shelters constructed specifically for generator use with no enclosed sides
– Elevated platforms that keep generators dry without enclosing any sides
Install and Maintain Essential Carbon Monoxide Detectors
Your carbon monoxide detectors serve as your last line of defense when prevention measures fail. Every home that uses a generator needs multiple battery-powered or battery-backup detectors—plug-in models become useless during the power outages when you need them most.
Non-Negotiable Detector Setup Requirements
- Place detectors near every sleeping area—CO poisoning often strikes while people sleep
- Install on every level of your home, including basements
- Test detectors monthly by pressing the test button—this 30-second habit could save your life
- Replace batteries annually—mark your calendar on a memorable date like New Year’s Day
- Replace entire units every 10 years—CO sensors degrade over time, even if the unit seems functional
Immediate Actions When CO Alarms Sound
When your carbon monoxide detector activates, you have precious seconds to act. The alarm means dangerous CO levels already exist—don’t investigate or try to find the source.
Follow this life-saving sequence:
1. Evacuate immediately—get everyone outside, including pets
2. Call 911 from outside your home
3. Stay outside—never re-enter until emergency responders declare it safe
4. Account for everyone—make sure all family members have evacuated
Master Safe Refueling Procedures to Prevent Multiple Hazards
Refueling a hot generator creates explosive risks beyond carbon monoxide poisoning. Gasoline vapors can ignite from hot engine parts, causing severe burns and fires that compound the danger.
Critical Refueling Safety Rules
- Wait 15-20 minutes for the generator to cool completely before refueling
- Use only approved fuel containers with safety features designed for gasoline storage
- Store fuel outside your home—never keep gasoline in your garage or living spaces
- Refuel in well-ventilated areas away from the house to avoid inhaling toxic fumes
Proper Electrical Connection Methods
Improper electrical connections create shock hazards and can lead to dangerous generator operation that increases CO risks.
Follow this connection priority:
1. Plug appliances directly into generator outlets when possible
2. Use heavy-duty outdoor extension cords rated for the wattage you’re drawing
3. Inspect all cords for damage before each use—frayed or cut cords create fire hazards
Require Professional Installation for Home Wiring Connections
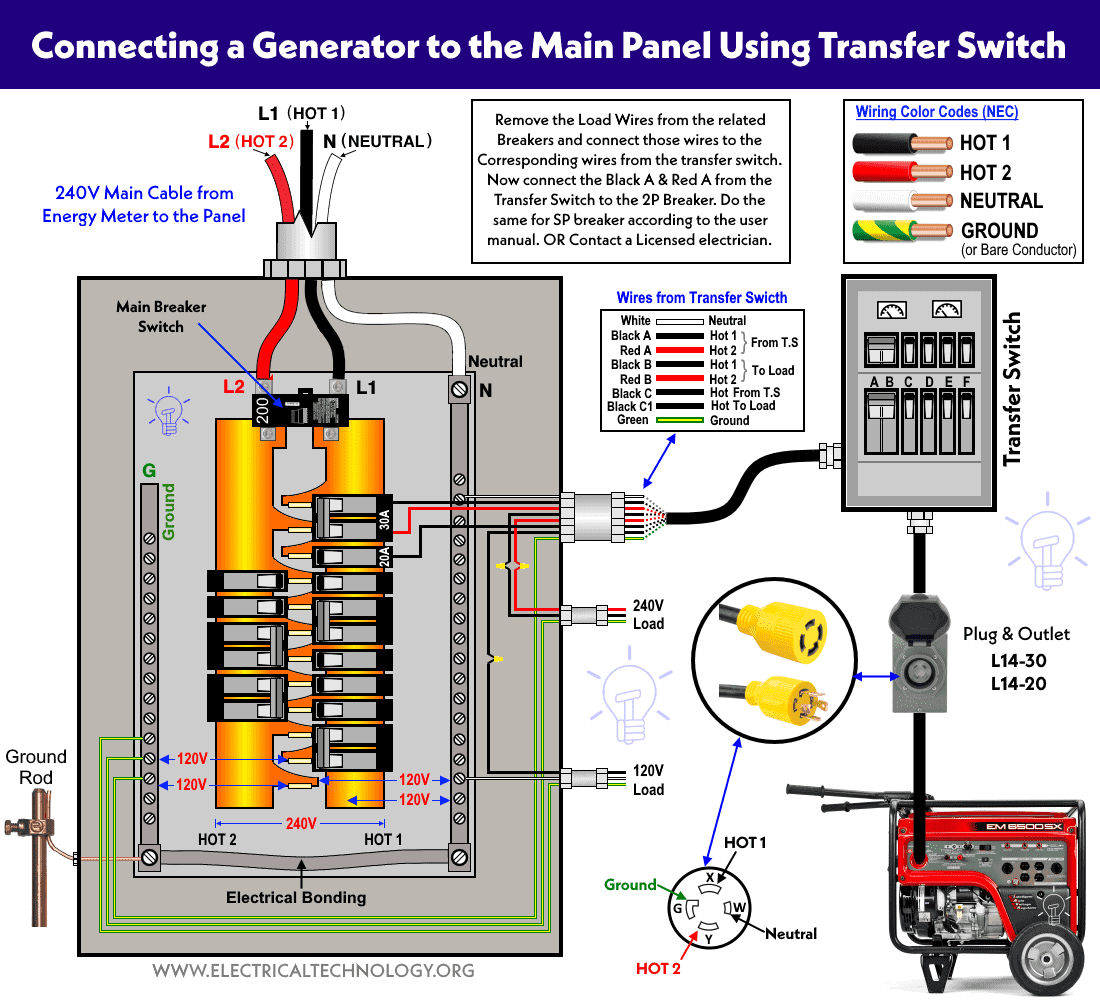
Connecting your generator to your home’s electrical system requires specialized knowledge. Improper installation creates backfeed hazards that can electrocute utility workers and cause generator malfunctions that increase CO risks.
Essential Professional Installation Requirements
- Hire only certified electricians with generator installation experience
- Install a transfer switch—this prevents dangerous backfeed into utility lines
- Ensure proper grounding—improper grounding creates electrical hazards
- Verify code compliance—installations must meet National Electrical Code standards
Identify All Carbon Monoxide Sources During Emergencies
Generators aren’t your only carbon monoxide threat during power outages. Multiple CO sources operating simultaneously create compounded risks that overwhelm safety systems.
Additional Emergency CO Threats to Monitor
- Vehicles running in attached garages—even with the door open
- Gas stoves or ovens used for heating—a common but deadly mistake
- Charcoal grills brought indoors—produces massive CO levels
- Propane camping heaters used without proper ventilation
Take this immediate action: During power outages, designate someone to check that no one is using alternative heat sources that produce carbon monoxide.
Recognize Early Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Symptoms
Early symptom recognition saves lives when prevention fails. Carbon monoxide poisoning symptoms mimic common illnesses, making awareness crucial during generator use.
Symptom Progression Timeline
- First 5-10 minutes: Headache, dizziness, nausea (often mistaken for flu)
- 15-30 minutes: Confusion, weakness, chest pain, vomiting
- 30-60 minutes: Loss of consciousness, stopped breathing
- Beyond 60 minutes: Brain damage or death
If multiple people in your household experience similar symptoms simultaneously, treat it as a carbon monoxide emergency immediately—don’t wait for confirmation.
Execute Emergency Response Protocol Within Seconds
Your response speed determines survival rates for carbon monoxide poisoning. Even mild exposure requires medical evaluation due to potential delayed complications.
Life-Saving Emergency Sequence
- Get everyone into fresh air immediately—open doors/windows as you exit
- Call 911 from outside—explain it’s a suspected CO poisoning
- Account for all family members—check everyone before re-entering
- Seek medical attention—even if symptoms seem to improve
- Wait for professional clearance—don’t return until emergency responders verify safety
Critical note: Carbon monoxide poisoning impairs judgment and physical ability. Designate someone to check on elderly neighbors or disabled family members during emergencies—don’t assume they’ll recognize symptoms.
Create Your Generator Safety Plan Before the Next Storm
Preparation prevents panic during power outages. Create your generator safety plan today—don’t wait until you’re in the middle of an emergency with failing power.
Essential Pre-Season Safety Checklist
- Install CO detectors with fresh batteries before storm season begins
- Practice safe placement—measure and mark the 20-foot distance from your home
- Purchase weather protection—get a generator-specific canopy before storms hit
- Educate all family members—ensure everyone knows the safety rules and emergency protocols
- Post emergency numbers—place 911 and poison control information near every phone
Carbon monoxide poisoning from generators remains one of the most preventable causes of death during natural disasters. Your generator provides essential power—don’t let it become your family’s greatest threat. Follow these safety measures religiously, and you’ll maintain both power and peace of mind during any emergency. Remember: when it comes to carbon monoxide, there are no second chances—your safety decisions today could save lives tomorrow.