Your generator sputters, struggles to start, or loses power unexpectedly—signs that point directly to a worn spark plug. Knowing how to change a spark plug on a generator restores reliable operation and prevents frustrating failures when you need backup power most. This essential maintenance task takes just 30 minutes and requires basic tools you likely already own. Whether you’re preparing for storm season or maintaining your RV’s emergency power, replacing this critical component ensures your generator delivers peak performance when it matters.
A faulty spark plug causes hard starting, rough running, and reduced power output. Ignoring this simple maintenance can lead to more serious engine problems and costly repairs. Follow this step-by-step guide to confidently replace your generator’s spark plug and keep your backup power system ready for action.
Critical Safety Shutdown Steps Before Spark Plug Replacement
Complete cool-down period: Wait at least 30 minutes after your generator stops running. Metal engine components retain dangerous heat that can cause severe burns during service.
Fuel system lockout: Turn the fuel valve to “OFF” and let the engine run until it stalls. This empties the carburetor and prevents dangerous fuel spills while working on your generator.
Electrical disconnection: Firmly grasp the spark plug boot (the rubber connector) and pull straight off—never yank the wire itself. This prevents damage to the ignition coil and accidental starting during service.
Work area setup: Position your generator on level ground in a well-ventilated space away from ignition sources. Keep a Class B fire extinguisher within arm’s reach for safety.
Locate Your Generator’s Exact Spark Plug Specifications

Find your model information: Check the data plate riveted to your generator’s frame or engine shroud. This plate contains your specific model and serial numbers essential for finding the correct replacement.
Manual reference: Your owner’s manual lists the exact spark plug part number—common examples include NGK BPR6ES or Champion RN9YC. These aren’t suggestions—they’re critical requirements for proper generator operation.
Verify these critical specifications:
– Thread size (typically 14mm for portable generators)
– Reach length (prevents dangerous piston contact)
– Heat range (manufacturer-specific for generator duty)
– Gap setting (usually 0.028″-0.031″ for most models)
Proper Generator Preparation for Spark Plug Service
Safe shutdown sequence:
1. Disconnect all electrical devices from your generator
2. Run generator 2-3 minutes without load to stabilize
3. Close fuel shutoff valve completely
4. Let engine stall naturally from fuel starvation
5. Turn ignition switch to OFF position
Access removal: Remove engine shrouds or side panels using Phillips screws or 10mm bolts. The spark plug sits at the cylinder head’s top or side, marked by a thick rubber boot. Clean the area around the plug with compressed air before proceeding.
Remove Your Old Spark Plug Without Damaging the Engine
Critical cleaning step: Blast compressed air around the spark plug well before removal. This prevents dirt from falling into your cylinder—a single grain of sand can destroy your engine.
Disconnection technique: Twist the boot slightly while pulling straight off. This breaks the seal without damaging the ignition wire connection.
Removal process:
1. Insert spark plug socket fully onto the hex
2. Turn counterclockwise slowly to break loose
3. Continue unscrewing by hand once threads release
4. Lift out old plug carefully for inspection
Diagnose Engine Health by Reading Your Old Spark Plug

Normal condition: Light tan or gray deposits with sharp electrode edges indicate healthy generator operation and proper fuel mixture.
Problem indicators to watch for:
– Black soot: Rich fuel mixture or restricted air filter
– Wet oil: Engine wear allowing oil into combustion chamber
– White blistering: Overheating from lean mixture or cooling issues
– Worn electrode: Gap exceeds 0.005″ from specification
Prepare Your New Spark Plug for Proper Installation
Gap verification: Check gap with feeler gauges even on “pre-gapped” plugs. Manufacturing tolerances vary, and incorrect gaps cause hard starting or poor generator performance.
Adjustment technique: Bend only the ground electrode (L-shaped piece) using gentle pressure. Never touch the center electrode or ceramic insulator—this can cause internal damage.
Thread treatment: Apply anti-seize compound sparingly to threads for aluminum heads. Skip this step for cast iron heads where seizing is less common.
Install Your New Spark Plug with Correct Torque
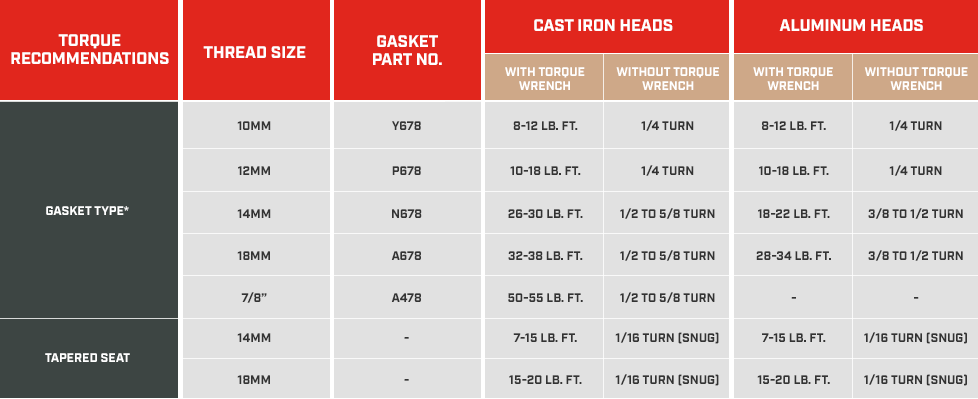
Hand-starting technique: Thread the new plug by hand for the first 3-4 turns. Any resistance indicates cross-threading—back out immediately and restart to avoid costly engine damage.
Torque specifications:
– Aluminum heads: 12-15 ft-lbs
– Cast iron heads: 20-25 ft-lbs
Without torque wrench: Turn 1/4 turn past finger-tight for used plugs, or 1/2 turn for new plugs with crush washers.
Boot connection: Apply dielectric grease to the inside of the spark plug boot. Push firmly until you hear/feel the click of full engagement—this ensures reliable electrical connection.
Test Your Generator After Spark Plug Replacement
Reassembly: Replace all covers and panels removed for access. Check oil level since spark plug service often coincides with routine maintenance.
Start-up procedure:
1. Open fuel shutoff valve
2. Set choke if engine is cold
3. Pull starter cord or use electric start
4. Let engine warm 5-10 minutes without load
Performance verification: Listen for smooth, consistent operation. Rough running or backfiring indicates installation issues or underlying problems revealed by the fresh spark plug.
Troubleshoot Common Spark Plug Replacement Issues
Hard starting solutions:
– Verify correct spark plug heat range and gap specification
– Check boot connection security and cleanliness
– Test ignition coil output with spark tester
– Examine fuel quality and carburetor condition
Rapid fouling diagnosis:
– Inspect air filter for severe clogging
– Check oil level—overfilling causes oil fouling
– Verify valve clearance and compression
– Assess fuel age and contamination
Generator Spark Plug Maintenance Schedule
Replacement intervals:
– Standard use: Every 100 hours or annually
– Heavy commercial use: Every 50 hours
– Seasonal equipment: Replace before first use each year
– Emergency backup: Inspect every 25 hours, replace as needed
Storage protocol: Before extended storage, run engine dry or add fuel stabilizer. Remove plug, add 2-3 drops of oil to cylinder, pull starter slowly to distribute, then reinstall plug without connecting wire.
Changing your generator’s spark plug takes just 30 minutes but delivers reliable power for hundreds of operating hours. This simple maintenance task prevents frustrating failures and extends your generator’s lifespan. Mark your calendar for the next change based on your usage pattern, and keep a correctly specified spare plug on hand for emergency replacement. Now that you know how to change a spark plug on a generator, you’ve taken a crucial step toward ensuring dependable backup power when you need it most.