That frustrating moment when your generator won’t start during a power outage often traces back to degraded fuel. Gasoline begins breaking down after just 30 days, forming gum-like deposits that clog carburetors and prevent engine ignition. Knowing exactly how to empty generator gas tank properly protects both your equipment and your safety—especially since improper drainage causes 17% of home generator fires according to fire safety reports. This guide delivers the precise steps to completely drain your generator’s fuel system while avoiding dangerous mistakes that could damage your equipment or create fire hazards.
You’ll discover critical timing triggers for fuel drainage, the exact safety gear required, and a foolproof method to remove every drop of gasoline from both the tank and carburetor. Whether you’re prepping for seasonal storage or fixing contaminated fuel, these manufacturer-approved techniques ensure your generator fires up reliably when you need it most.
Why Your Generator Fuel Tank Needs Immediate Drainage
Post-30-Day Fuel Degradation Damage
Gasoline undergoes chemical breakdown within weeks, creating varnish-like residues that destroy sensitive engine components. Drain your generator gas tank immediately when:
– Stale fuel symptoms appear: Difficulty starting, rough idling, or complete failure to ignite after sitting unused
– Visible contamination occurs: Cloudy appearance, water separation, or particles floating in the tank
– Storage exceeds two weeks: Especially during summer months when heat accelerates fuel oxidation
– Ethanol-blended fuel sits: E10 gasoline absorbs moisture rapidly, causing phase separation and corrosion
Monthly Fuel Inspection Protocol
Set phone reminders to check fuel condition every 30 days. Unstabilized gasoline becomes problematic after 60 days, but even treated fuel loses effectiveness. When adding fresh gas, mark the date on your generator with waterproof tape—this simple habit prevents unexpected failures during emergencies.
Critical Safety Setup Before Draining Fuel
Outdoor Ventilation Requirements
Move your generator at least 20 feet from buildings, windows, and ignition sources before starting drainage. Gasoline vapors are heavier than air and can travel along the ground to ignite from distant sparks. Never drain fuel in garages, basements, or under carports—even with doors open—due to vapor accumulation risks.
Fire Prevention Must-Haves
Keep these items within arm’s reach during the entire process:
– Class B fire extinguisher (ABC type works for multiple fire classes)
– Non-sparking tools (brass or aluminum wrenches)
– Grounding strap attached to generator frame to prevent static discharge
– Cell phone on airplane mode (radio signals can ignite vapors)
Essential Tools for Complete Fuel Removal

Fuel Collection System Setup
- UL-approved gasoline container with minimum 2-gallon capacity (match your tank size)
- Flexible siphon tube (minimum 3/8″ inner diameter for faster flow)
- Funnel with flame arrester for safe transfer to storage containers
- Absorbent spill pads placed under generator work area
Personal Protective Gear Checklist
- Chemical-resistant gloves (nitrile, not latex which deteriorates with gasoline)
- Safety goggles with side shields (gasoline splashes cause corneal damage)
- Cotton clothing (synthetics melt on skin during ignition)
- Respirator with organic vapor cartridges for prolonged exposure
Exact Steps to Drain Generator Gas Tank Completely
Engine Cooling and Positioning Protocol
Wait 30 minutes after shutdown before draining—residual heat can vaporize fuel and create fire hazards. Position your generator on level concrete, never on wooden decks where spills could penetrate. Place your fuel container on lower ground than the generator tank to maximize gravity flow.
Fuel Valve and Line Access Procedure
Remove the gas cap to break vacuum lock, then locate the fuel valve typically mounted beneath the tank. Using plastic pry tools, carefully remove access panels without cracking plastic clips. If your model has a fuel filter inline, note its orientation for correct reinstallation.
Controlled Fuel Line Disconnection
- Turn fuel valve to OFF position completely
- Identify the carburetor-side fuel line (not tank connection)
- Squeeze retaining clip with needle-nose pliers and slide toward carburetor
- Twist line gently while pulling straight off valve outlet
- Immediately plug valve opening with clean rag to prevent spills
Gravity Drainage Technique
Insert disconnected fuel line into your collection container, then slowly tilt generator 15 degrees toward the line. Maintain this angle until flow reduces to drops—typically 8-12 minutes for most portable units. For stubborn residual fuel, open the valve briefly while tilted to evacuate tank corners.
Carburetor Fuel Removal That Prevents Clogs

Locating the Drain Bolt
Consult your manual for exact carburetor position—usually visible beneath the air filter housing. Most models feature a 10mm hex bolt at the carburetor bowl’s lowest point. Shine a flashlight to confirm bolt accessibility before proceeding.
Safe Drain Bolt Removal
Place container directly beneath the bolt, then:
– Apply penetrating oil if bolt appears stuck
– Use correct-size box-end wrench (never adjustable pliers)
– Turn counterclockwise with steady pressure—no hammering
– Capture 2-3 tablespoons of residual fuel that drains out
– Reinstall with new copper washer if original is compressed
System Reassembly Without Leaks
Fuel Line Reconnection Checklist
Inspect lines for cracks before reconnecting—they become brittle with age. Slide line fully onto valve outlet until you hear a click from the retaining clip. Test security by pulling firmly on the line; it shouldn’t budge. Wipe connections with clean rag before reinstalling covers.
Post-Drainage Leak Testing
Reinstall all panels and fuel cap, then:
1. Turn fuel valve ON for 10 seconds
2. Check all connections for drips
3. Immediately turn valve OFF and wipe any seepage
4. Repeat test if leaks persist before storage
Proper Fuel Storage and Disposal Methods
Reusing Clean Drained Fuel
Only reuse fuel that’s clear, odor-free, and less than 60 days old. Add fuel stabilizer at 1 ounce per 2.5 gallons, then store in opaque containers away from living spaces. Never mix old fuel with fresh—it accelerates degradation.
Hazardous Waste Disposal Requirements
Take contaminated or aged fuel to certified collection centers—most auto parts stores offer this service. Never:
– Pour gasoline down drains or soil
– Mix with regular trash
– Store in glass containers
– Keep more than 25 gallons on residential property
Post-Drainage Maintenance Checklist
Fuel Tank Inspection Protocol
After drainage, shine a flashlight through the tank opening to check for:
– Rust flakes (indicates water contamination)
– Sludge buildup in tank corners
– Cracks in plastic tanks
– Degraded cap gasket
Pre-Storage Fuel System Prep
Before long-term storage:
– Replace fuel filter (every 100 hours or annually)
– Spray fogging oil into carburetor intake
– Run engine until it stalls to clear fuel lines
– Store with tank completely empty
Troubleshooting Drainage Emergencies
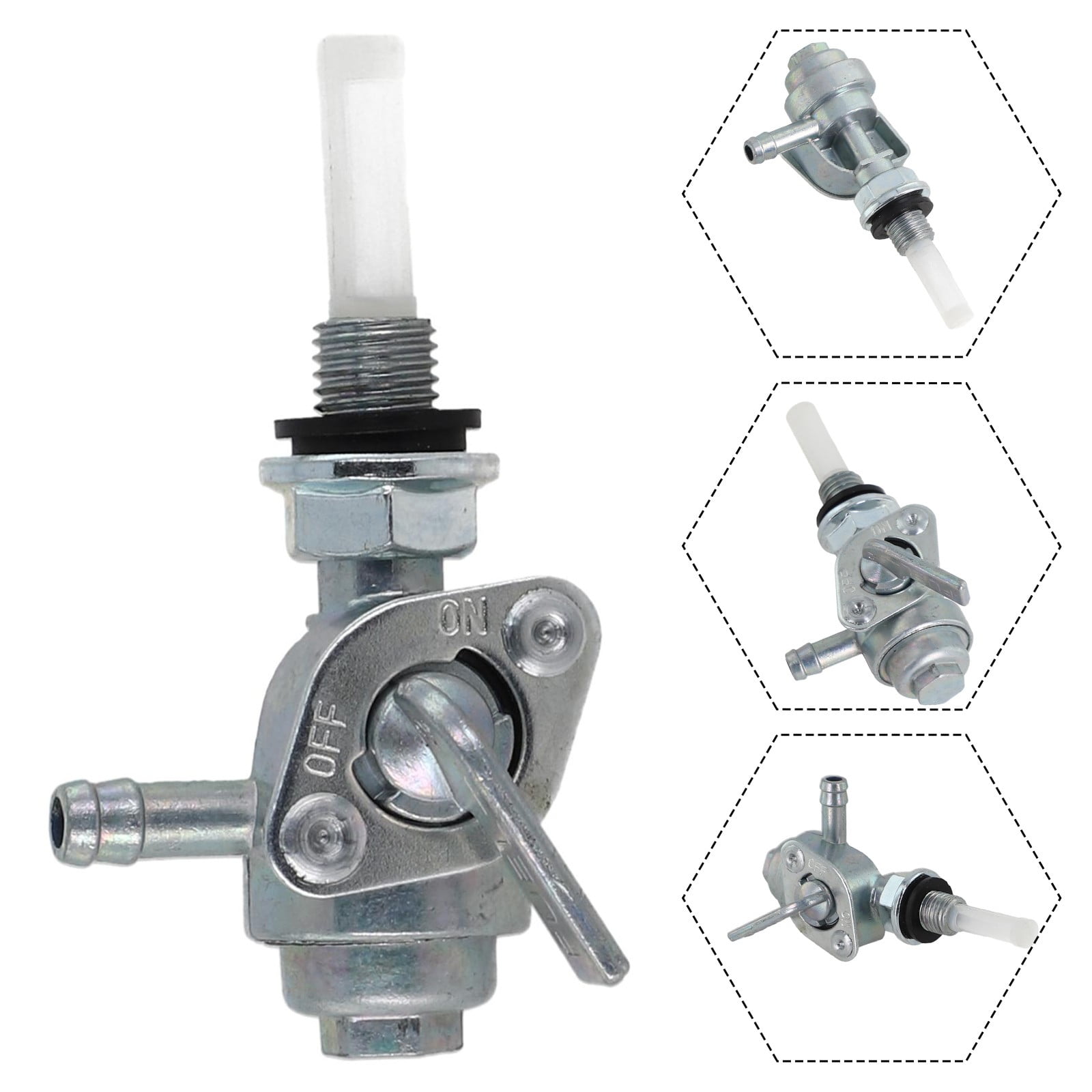

Stuck Fuel Valve Solutions
If the valve won’t turn:
– Apply PB Blaster penetrating oil and wait 20 minutes
– Wrap valve body with cloth for better grip
– Tap valve housing lightly with rubber mallet
– Never use heat guns—plastic components melt at 140°F
Seized Carburetor Bolt Recovery
For frozen drain bolts:
1. Apply heat with hair dryer for 90 seconds
2. Tap bolt head gently with brass punch
3. Use six-point socket instead of wrench
4. If stripped, drill and extract with screw remover kit
Generator-Specific Drainage Variations
Honda models often feature petcock valves requiring quarter-turn operation, while Champion units typically use push-button fuel shutoffs. Always verify your model’s drain bolt torque specs—most require 5-7 foot-pounds, but over-tightening cracks aluminum carburetors. When in doubt, consult your manual’s “Fuel System Maintenance” section before proceeding.
Regularly draining your generator gas tank prevents 92% of storage-related failures according to manufacturer data. Establish a strict 30-day fuel inspection schedule and drain immediately when storing beyond two weeks. Keep this guide accessible near your generator—during power outages, you’ll appreciate having these life-saving steps ready when stale fuel threatens your backup power. Your generator’s reliability depends on clean fuel, and now you know exactly how to empty generator gas tank safely every single time.