That bone-rattling 90+ dB roar from your generator’s exhaust isn’t just annoying—it violates campground noise ordinances, ruins backyard gatherings, and can trigger HOA fines. While engines produce mechanical noise, the exhaust system emits the sharpest, farthest-traveling frequencies. The good news? You can slash 15-25 dB from your generator’s exhaust note using field-tested methods costing under $50. This guide reveals exactly how to make a generator exhaust quieter using real-world solutions from professional acoustics tests and DIY community builds.
Thrush Glass-Pack Muffler Swap: 30-Minute 10 dB Fix
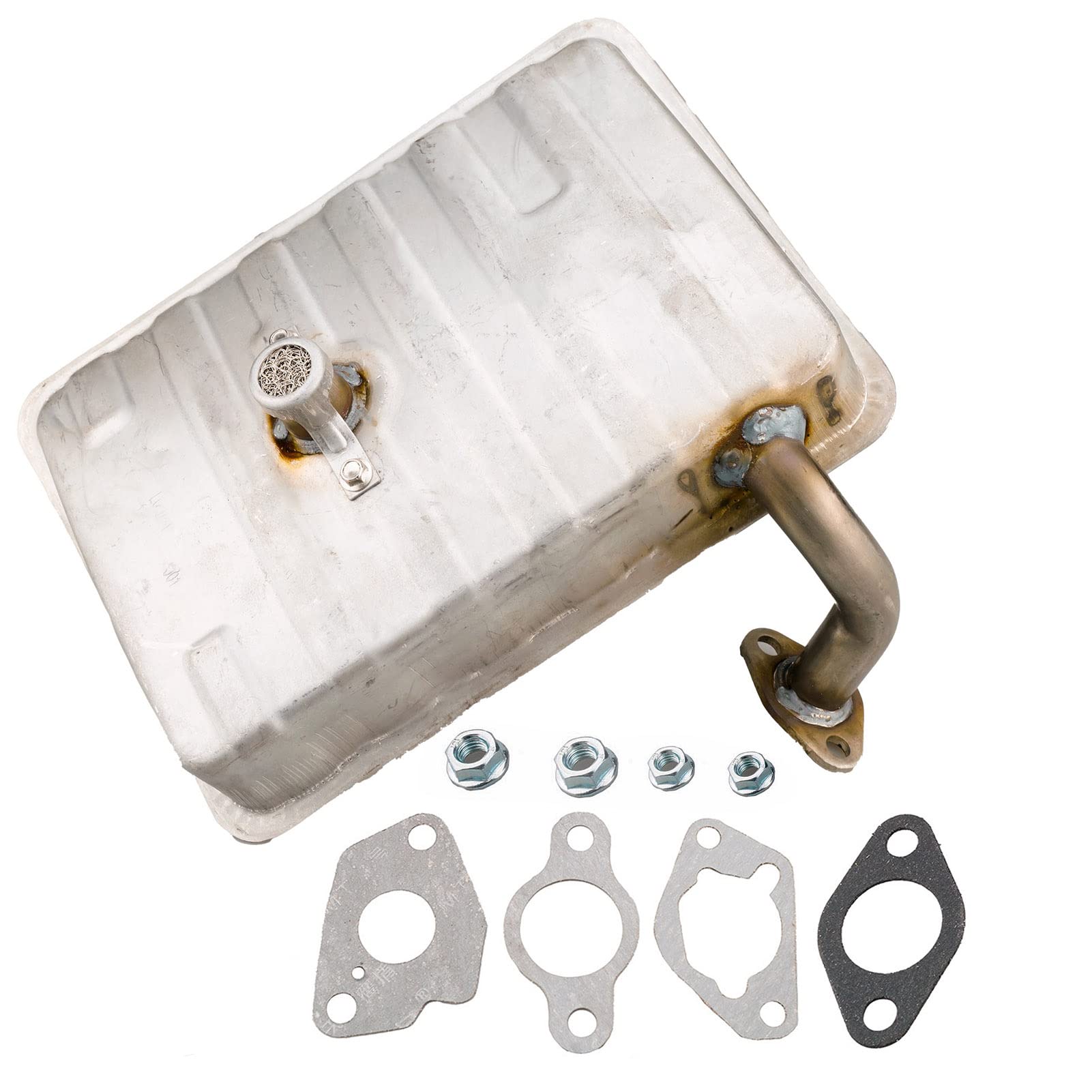

Most portable generators ship with flimsy, undersized mufflers prioritizing cost over noise reduction. Replacing yours with a Thrush glass-pack muffler delivers the biggest exhaust noise reduction per dollar—verified by field tests across Kipor 3500W, Coleman 5000W, and Briggs 15HP units. Users consistently report 8-15 dB drops at 7 meters, transforming a disruptive roar into a background hum.
Why This Works
Glass-pack mufflers contain steel wool or fiberglass packing that disrupts exhaust pressure pulses without excessive back-pressure. Unlike performance automotive mufflers, they maintain compact dimensions critical for portable generators. Crucially, they tolerate the high exhaust temperatures (500°F+) that melt foam-based alternatives.
Installation Checklist
– Remove stock muffler: Typically secured by two bolts—spray with penetrating oil if corroded
– Match pipe diameters: Most generators use ¾-1 inch outlets (measure yours with calipers)
– Connect with flex pipe: Use 1-inch stainless steel flex hose ($8 at auto stores) for vibration absorption
– Secure with clamps: Double-clamp all joints using 304 stainless steel bands (avoid zip ties—they melt)
Pro Tip: Keep your original muffler bolted to the generator frame. The glass-pack adds 8 inches of length, but you can swap back in 5 minutes for true portability during camping trips. Always verify back-pressure stays under 1 PSI using a manometer—exceeding this destroys small engines.
Vertical Exhaust Pipe: 6 dB Ground-Level Reduction
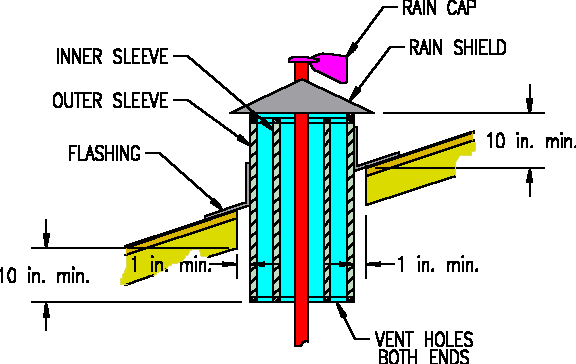
Directing exhaust skyward exploits physics: sound energy dissipates faster upward than along the ground. This movie-industry trick drops perceived noise by 6-8 dB at ear level—enough to turn “unbearable” into “background hum” for neighbors.
10-Foot Pipe Installation Guide
Materials You Need
– 10 feet of 1-inch galvanized EMT conduit (hardware store)
– High-temp silicone sealant (rated 500°F+)
– 90-degree elbow + rain cap (critical for moisture prevention)
– 12-inch flex section (for vibration isolation at generator)
Critical Steps
1. Attach flex hose directly to muffler outlet using two clamps
2. Thread rigid pipe upward through the 90-degree elbow
3. Seal all joints with high-temp silicone—standard tape fails at exhaust temps
4. Top with rain cap to prevent water ingress (a leading cause of generator failure)
5. Secure pipe with guy wires if over 8 feet tall
Stealth Upgrade: Paint the pipe matte black and position against dark fences or trees. Field testers confirm this makes exhaust virtually invisible from 25+ feet while directing noise away from living areas. Never angle pipes horizontally—this traps heat and violates fire codes requiring 2+ feet clearance from combustibles.
Water Injection System: 20 dB Quiet-Down for Permanent Sites
Marine engineers have silenced boat engines for decades using water-injected exhausts. This method collapses high-pressure exhaust pulses by bubbling them through water, achieving 15-25 dB reduction—more than any muffler swap. Alberta cabin owners report generators becoming “barely audible” at 50 feet with this setup.
5-Gallon Bucket Build (Under $15)
Why It Works: Water absorbs acoustic energy from exhaust pulses while steam cools gases. HDPE buckets resist corrosion better than metal alternatives.
Materials Checklist
– 5-gallon HDPE bucket (NOT metal—it rusts fast)
– 1-inch radiator hose rated 300°F+
– 1-inch hose barb fitting
– High-temp silicone sealant
– 1/8-inch drill bit (for siphon break)
Step-by-Step Setup
1. Drill 1-inch hole 2 inches from bucket bottom
2. Insert hose barb and seal with silicone (let cure 24 hours)
3. Fill bucket ¾ full with water
4. Route exhaust hose downward into water (never let water level drop below inlet)
5. Drill 1/8-inch vent hole in hose above water line to prevent back-siphon on shutdown
Critical Safety Notes
– Water loss: Expect 1 gallon per 12 hours at full load—use an RV float valve for auto-refill
– Backflow prevention: Position bucket below exhaust outlet height
– CO risk: Always place system outdoors with wind-direction monitoring—never use in enclosed spaces
Intake Silencing: Fix the Overlooked Noise Source

Many DIYers miss that generator air intakes produce 85+ dB “chuffing” sounds that travel like exhaust noise. A $20 compressor intake silencer reduces this by 3-6 dB—critical for full-spectrum quieting.
Universal Compressor Silencer Install
- Locate air horn (usually atop engine)
- Unscrew existing cover (typically ¼-½ inch NPT threads)
- Screw in automotive compressor silencer ($12 at truck parts stores)
- Confirm no airflow restriction—engine must breathe freely
DIY Alternative: Pack stainless steel wool inside a 6-inch section of 2-inch PVC pipe. Press-fit over intake horn and replace wool annually as it compacts. Never use cotton or fiberglass—they shed particles into the engine.
Safety Essentials Every Builder Must Know
Back-Pressure Limits
Most small engines tolerate ≤1 PSI at the exhaust port. Exceeding this causes overheating and piston damage. Test with a manometer:
– Attach gauge to muffler inlet
– Run generator at 50% load
– Readings above 1 PSI require larger-diameter piping
Fire Prevention Checklist
- Maintain 24-inch clearance between exhaust components and wood/dry grass
- Use high-temp silicone (not RTV) for all seals—standard sealants ignite at 400°F+
- Install battery-powered CO alarms 5 feet from exhaust outlets
Vibration Killers
Exhaust noise transmits through frames into the ground. Add 50-70 durometer rubber mounts under your generator to block 8-12 dB of structure-borne noise. For units over 250 lbs, spring isolators provide 15-20 dB reduction at 60 Hz.
| Method | Cost | dB Reduction | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thrush Muffler | $30 | 8-15 dB | Camping, emergencies |
| Vertical Pipe | $25 | 6-8 dB | Backyard use |
| Water Injection | $15 | 15-25 dB | Cabins, permanent sites |
| Intake Silencer | $20 | 3-6 dB | All generators |
Final Setup Checklist
Start with the Thrush muffler swap—it’s the highest-impact first step. Test noise levels at 7 meters before and after (free apps like Decibel X work). Next, add vertical piping to push sound skyward. For permanent installations, integrate water injection while monitoring back-pressure. Finally, silence the intake with a compressor silencer. Always verify temperatures stay within spec—add a 120mm PC fan if cylinder heads exceed 200°F. With these exhaust-specific fixes, your generator will run at conversation levels (65 dB) from 20 feet—keeping neighbors happy without sacrificing power. Remember: never compromise on back-pressure limits or CO safety. A quiet generator is useless if it destroys your engine or endangers lives.