Your generator’s battery is its heartbeat—without the right one, your backup power system fails when you need it most. Many homeowners and facility managers learn this the hard way during emergencies when a dead or undersized battery leaves them without power. Whether you’re replacing a failed unit or sizing one for a new generator, this guide reveals exactly how to select battery for generator applications that deliver reliable starts in any condition. You’ll discover critical specifications most buyers overlook, decode confusing battery labels, and match the perfect chemistry to your specific generator model and usage patterns.
Match Battery Chemistry to Your Generator Type

Why AGM Batteries Dominate Home Standby Systems
AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries have become the gold standard for residential generators due to their maintenance-free operation and superior vibration resistance. Unlike conventional flooded batteries requiring monthly water checks, AGM units seal electrolyte in fiberglass mats—making them spill-proof in any orientation while delivering 5-7 years of service life. They provide enough Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) for quick engine starts while tolerating the occasional deep discharge if your generator sits idle for months.
Flooded lead-acid batteries remain viable for budget-conscious buyers, but they demand regular electrolyte level checks and specific gravity testing. For hard-to-access installations like basement generators, the higher upfront cost of AGM pays off through eliminated maintenance visits. Expect to pay $220-$320 for a Group 31 AGM battery versus $120-$180 for a comparable flooded unit.
When Lithium Iron Phosphate Justifies the Premium
Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO₄) batteries deliver game-changing benefits for specific applications despite costing 3-5 times more than lead-acid alternatives. If your generator serves as part of a solar hybrid system or cycles daily, lithium’s 2,000-5,000 deep cycles versus 500-1,000 for lead-acid makes it cost-effective over time. These batteries operate reliably in extreme temperatures from -20°C to 60°C and weigh 50-70% less—critical for portable generators used in remote locations.
The thermal-runaway threshold exceeding 270°C makes LiFePO₄ exceptionally safe compared to other lithium chemistries. For vacation homes where maintenance isn’t possible or critical facilities needing maximum reliability, the 10-year lifespan offsets the higher initial investment. Always verify your generator’s charger compatibility before switching to lithium, as they require specific voltage profiles.
Decode Critical Battery Specifications

Calculate Your Exact CCA Requirements
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) represent your battery’s ability to start the generator in freezing conditions—the single most overlooked specification during selection. The industry standard defines CCA as the current a battery can deliver for 30 seconds at -17.8°C while maintaining at least 7.2 volts per 12V cell. Undersizing this specification causes slow cranking and eventual starter coil burnout.
Use this engine-specific formula: Engine displacement (liters) × 125 = minimum CCA. A 5.7L generator engine needs approximately 712 CCA minimum. For diesel engines in cold climates, multiply by 1.5-2.0—making that same 5.7L diesel require up to 1,068 CCA at -20°C. Always oversize by 15-20% to account for battery degradation over time; a battery operating at just 70% of rated CCA may fail to start your generator during winter emergencies.
Determine Correct Voltage Architecture
Generator size dictates your voltage requirements: small residential units use 12V systems with a single battery, while mid-size commercial generators (15-200 kW) require 24V systems using two 12V batteries wired in series. Large industrial units exceeding 2 MW may need 32-48V DC configurations. Never mix battery types, ages, or capacities in series configurations—this creates dangerous imbalances that accelerate failure.
Measure your battery tray dimensions before ordering. Industry-standard Group sizes include:
– Group 24: 260×173×225 mm (70-85 Ah) for 4-7 kW generators
– Group 31: 330×173×240 mm (95-125 Ah) for 15-22 kW units
– 8D: 527×283×250 mm (220-280 Ah) for industrial applications
Avoid Critical Compatibility Mistakes
Verify Terminal Configuration Before Buying
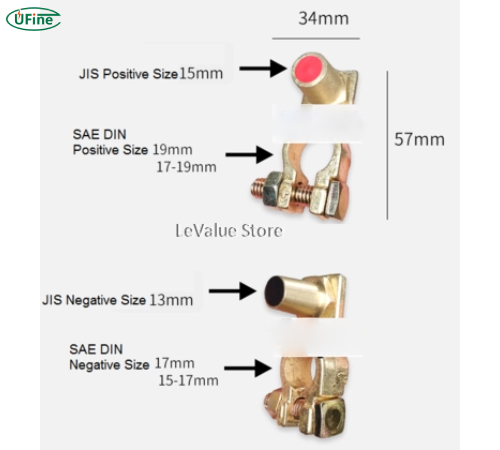
Mismatched terminals cause installation disasters—measure your existing cable reach and stud height before purchasing. Automotive SAE posts, M6/M8 threaded studs, or dual terminals must match exactly. Reverse polarity connections instantly damage starter solenoids, so confirm positive/negative orientation matches your generator’s wiring diagram. Some aftermarket batteries feature taller terminals that prevent proper cable installation in tight compartments.
Confirm Charger Compatibility
Lead-acid batteries require 14.4V absorption and 13.6V float voltages with temperature compensation, while lithium iron phosphate needs 14.6V absorption and built-in low-temperature cutoff below 0°C. Upgrading to lithium may necessitate replacing your charger—a $50-$150 expense many buyers overlook. Flooded batteries demand proper ventilation (0.5 m³ per 100 Ah for hydrogen gas dispersion), while AGM and lithium units operate safely in enclosed spaces.
Installation and Maintenance Essentials
Proper Mounting Prevents Premature Failure
Secure batteries with hold-downs preventing more than 1 inch of movement in any direction. For mobile applications, use vibration-isolating mounts to protect internal components from damage. In 24V systems, install batteries side-by-side with equal cable lengths to prevent voltage imbalances—never place one battery directly above the other.
Size cables for maximum 3% voltage drop during cranking. Clean terminals with a wire brush before connection and apply a thin petroleum jelly coating to prevent corrosion. Torque connections to manufacturer specifications—over-tightening cracks battery posts while under-tightening causes dangerous arcing.
Follow Chemistry-Specific Maintenance
AGM and flooded batteries need monthly voltage checks; resting voltage below 12.6V indicates undercharging. Perform semi-annual load testing at 50% CCA for 15 seconds—voltage drop exceeding 1.0V signals replacement time. Flooded batteries require electrolyte level checks above the plates and specific gravity testing (1.265 ± 0.010 at 25°C).
Lithium iron phosphate batteries need minimal maintenance—quarterly connection checks and annual capacity testing. Never store lithium batteries at 100% charge; maintain 40-50% state of charge for extended storage to maximize calendar life. Replace lead-acid batteries when CCA drops below 70% of rating or after 3+ years, while lithium units warrant replacement at 80% capacity or 8+ years.
Quick Reference Sizing Guide
7 kW Home Generator: Group 27 AGM, 12V 525 CCA, 92 Ah—fits standard trays with 5-7 year service life
22 kW Whole-House: Group 31 AGM, 12V 700 CCA, 100 Ah—handles larger engines with reserve capacity
750 kVA Industrial: Dual 8D AGM in series, 24V 1,600 CCA, 240 Ah each—meets industrial specifications
3 kW Solar Hybrid: 12V LiFePO₄ 100 Ah—cycles daily with 10-year lifespan for off-grid applications
Final Selection Checklist
Before purchasing, verify these six critical factors:
1. OEM specifications for exact voltage, CCA, and Group size from your generator manual
2. Chemistry choice based on maintenance tolerance and budget (AGM balance vs lithium longevity)
3. Terminal compatibility with existing cables and polarity configuration
4. Charger requirements—especially critical when upgrading to lithium
5. Replacement pairs for 24V systems to prevent imbalance issues
6. Warranty registration immediately after installation for lifecycle tracking
Selecting the right generator battery ensures reliable power when the grid fails. By matching CCA requirements to your engine size, choosing chemistry based on maintenance preferences, and verifying physical compatibility, you’ll avoid the most common selection mistakes. With proper installation and maintenance, expect 5-10 years of dependable service from your generator battery investment—keeping your critical systems powered through every emergency.